Designing Cisco Enterprise Networks (ENSLD) Questions and Answers
A customer reports that each time a networking component fails, OSPF recalculates the backup path, with causes a short outage. Which solution must the customer implement to improve this situation?
A network engineer must design an MSDP multicast solution to provide RP resilience in a network with two separate domains. Also, multicast sources and receivers must register with the local RP. Which solution must the engineer choose?
An architect must address sustained congestion on the access and distribution uplink of network. QoS has already been implemented and optimized, but it is no longer effective in ensuring optimal network performance. Which two solutions should the architect use to improver network performance? (Choose two)
At which layer does Cisco Express Forwarding use adjacency tables to populate addressing information?
In an SD-WAN architecture, which methods are used to bootstrap a vEdge router?
Which two routing protocols allow for unequal cost load balancing? (Choose two.)
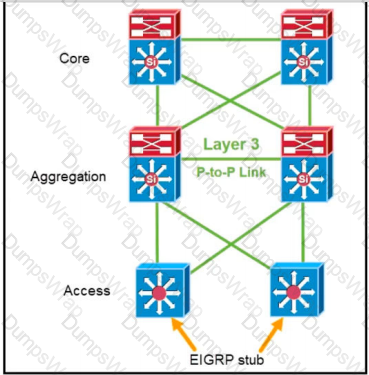
Refer to the exhibit. Where must an architect plan for route summarization for the topology?
What is the purpose of a control plane node in a Cisco SD-Access network fabric?
What is the function of the multicast Reverse Path Forwarding check?
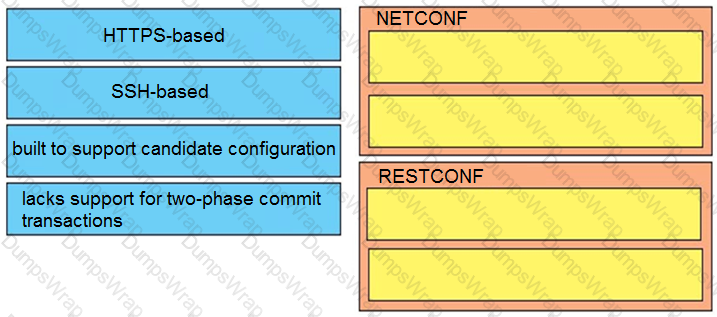
Drag and drop the properties from the left onto the protocols they describe on the right.
Which function do reverse path forwarding mechanisms perform in a multicast deployment?
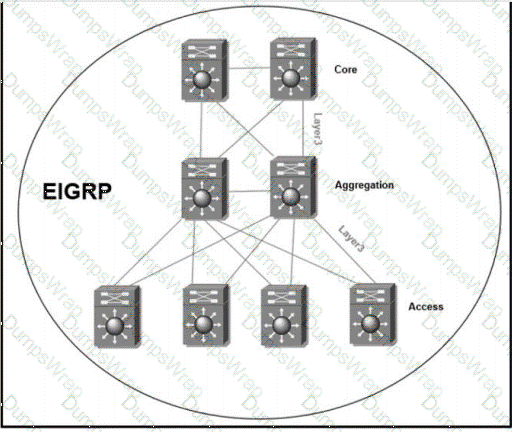
Refer to the exhibit. The full EIGRP routing table is advertised throughout the network. Currently, users experience data loss when any one link in the network fails. An architect optimizes thenetwork to reduce the impact when a link fails. Which solution should the architect include in the design?
A network administrator is troubleshooting a DMVPN setup between the hub and the spoke. Which action should the administrator take before troubleshooting the IPsec configuration?
An engineer is designing a multicast network for a company specializing in VoD content. Receivers are across the Internet, and for performance reasons, the multicast framework close to the receivers within each AS. For high availability, if the sources in one AS are no longer available, the receivers of that AS must be able to receive the VoD content from sources in another AS. Which feature must the design include?
Which node performs the LISP Map-Server and Map-Resolver functions in the Cisco SD-Access network architecture?
An engineer must design a VPN solution for a company that has multiple branches connecting to a main office. What are two advantages of using DMVPN instead of IPsec tunnels to accomplish this task? (Choose
two.)
Which two statements about VRRP object tracking are true? (Choose two)
An engineermustdesign a management network for a customer's enterprise network. The design must:
- provide the ability to grant and revoke access privileges
- allow only protocols SSH, NTP, FTP, and SNMP
- restrict access to management Interfaces
Which solution must the engineer choose to meet the requirements?
An engineer is working for a large cable TV provider that requires multiple sources streaming video on different channels using multicast with no rendezvous point. Which multicast protocol meets these requirements?
Which design achieves SD-WAN control plane redundancy?
Refer to the exhibit.
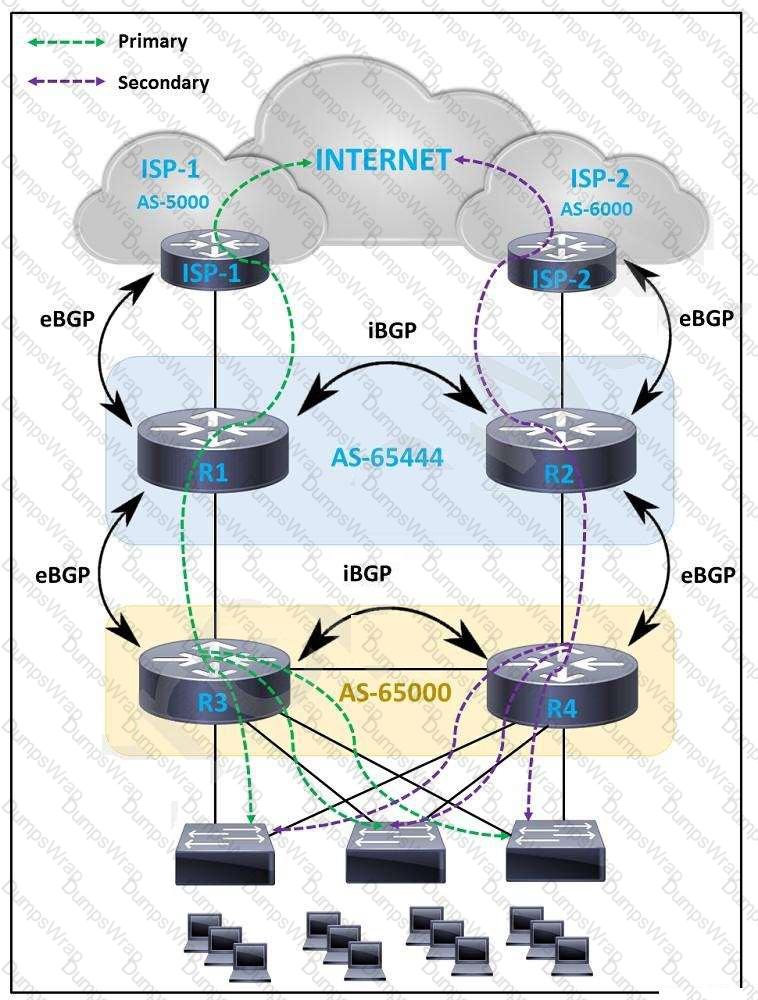
An engineer must design a WAN solution so that ISP-1 is always preferred over ISP-2. The path via ISP-2 is
considered as a backup and must be used only when the path to ISP-1 is down. Which
solution must the engineer choose?
How is end-to-end microsegmentation enforced in a Cisco SD-Access architecture?
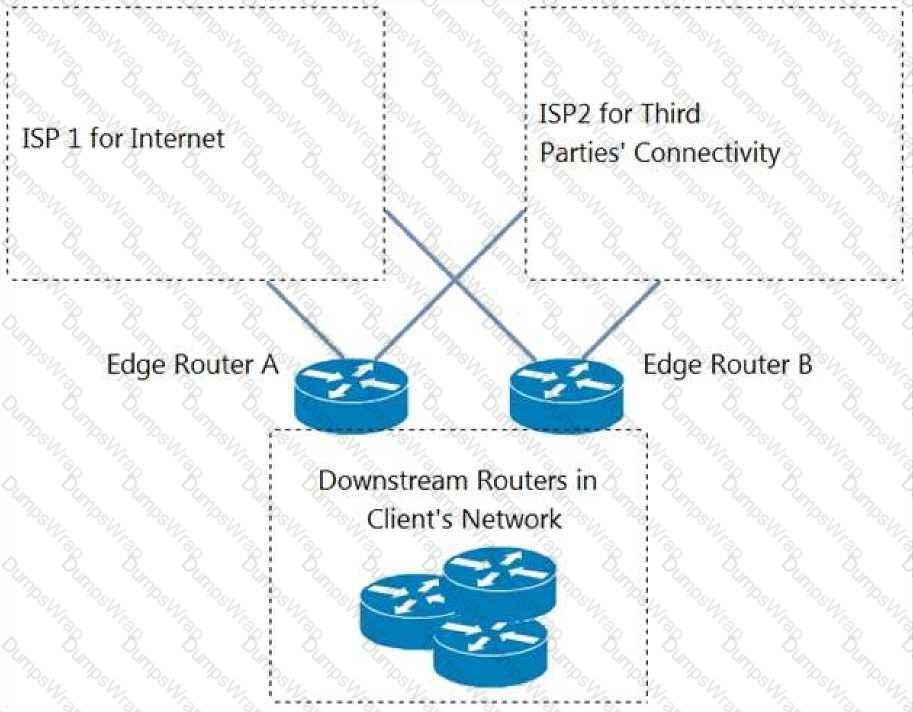
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is designing a BGP solution for a client that peers with ISP1 for full Internet connectivity and with ISP2 for direct exchange of routes for several third parties. Which action, when implemented on the edge routers, enables the client network to reach the Internet through ISP1?
Company A recently acquired another company. Users of the newly acquired company must be able to access a server that exists on Company A’s network, both companies use overlapping IP address ranges. Which action conserves IP address space and provides access to the server?
A network engineer must segregate three interconnected campus networks using IS-ISrouting. A two-layer hierarchy must be used to support large routing domains and to avoid more specific routes from each campus network being advertised to other campus network routers automatically. Which two actions does the engineer take to accomplish this segregation? (Choose two.)
An architect must develop a campus network solution that includes:
logically segmented and isolated networks
ability to communicate between network segments when required
support for overlapping IP addresses
widely available technologies to avoid purchasing specialized equipment
Which solution must the architect select?
Which type of rendezvous point deployment is standards-based and supports dynamic RP discovery?
Which control-plane technology allows the same subnet to exist across multiple network locations?
A company is running BGP on a single router, which has two connections to the same ISP. Which BGP
feature ensures traffic is load balanced across the two links to the ISP?
An organization is designing a detailed QoS plan that limits bandwidth to specific rates. Which two parameters are supported be the traffic policing feature? (Choose two.)
Which two functions is the Cisco SD-Access Edge Node responsible for? (Choose two.)
An engineer must design a multicast network for a financial application. Most of the multicast sources also receive multicast traffic (many-to-many deployment model). To better scale routing tables, the design must not use source trees. Which multicast protocol satisfies these requirements?
A router running ISIS is showing high CPU and bandwidth utilization. An engineer discovers that the router is configured as L1/L2 and has L1 and L2 neighbors. Which step optimizes the design to address the issue?


