Implementing Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing Solutions Questions and Answers
Refer to the exhibit.

Which task must you perform on interface g1/0/0 to complete the SSM implementation?
Refer to the exhibit.
All routers on this network have been configured with P1M-SM and R1 is the rendezvous point However, when asymmetric routing is implemented to modify link usage the network begins to drop certain multicast traffic Which action corrects the problem?
A network consultant is troubleshooting IS-IS instances to identify why a routing domains is having communication problems between the two instances. Which description of the possible cause of issues in the routing domain is true?

Refer to the exhibit. Which duplicate configuration causes this message during setup of an MPLS BGP network?
What are two features of dual-stack? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit.
 .
.
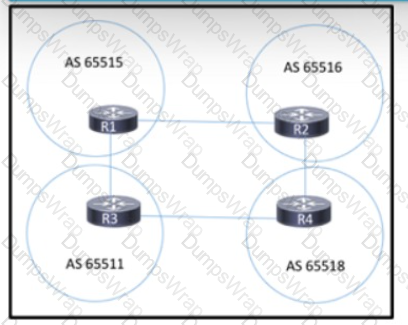
R1 is expected to receive routes originating from AS 65516 and from any ASs that are directly attached to it. However, R1 is receiving routes only from AS 65516. Which action corrects the configuration?
How does SRv6 function on the control plane?
Refer to the exhibit.
A network engineer configured routers R1 and R5 to run in IS-IS Level 1 mode and router R6 to run in IS-IS Level 2 mode. All other routers are running as Level 1 / Level 2 routers. An engineer expects traffic from R1 to R6 to pass via R2, but IS-IS routing has calculated the best path via R4. Which action corrects the problem?
Refer to the exhibit.
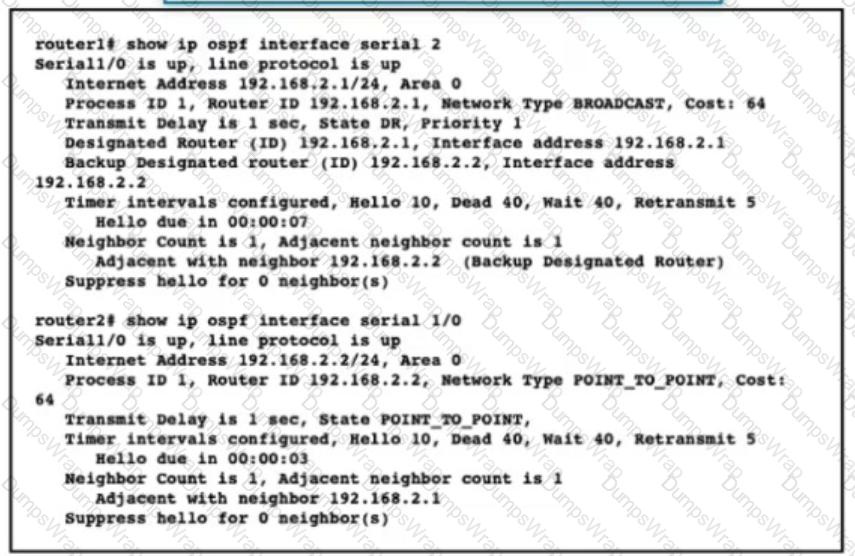
Router 1 and Router2 have shared routes in the OSPF database but the routes are missing from their routing tables. Checking me prefix-list configuration on both routers, the engineer confirmed all networks are allowed What action should the engineer take to fa the problem?
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1. R2, R3. and R4 are peer routers that reside in different administrative domains. PIM-SM is running in each autonomous system, and EBGP is configured between the peers. A network administrator has just implemented MSDP between the connected peers. When the administrator enabled the MSDP configuration. R1 and R2 failed to establish a peering relationship. All other connected routers successfully established peering sessions Which action must the engineer take to resolve the issue between R1 and R2?
Which difference should be considered when intradomain or interdomain multicast routing is implemented?
Refer to the exhibit.
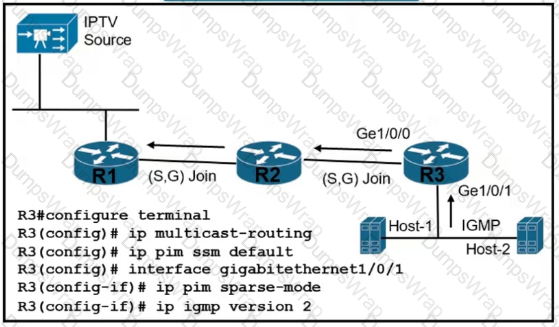
A customer reports that Host-1 is failing to receive streaming traffic from the IPTV source. The engineer has confirmed that hosts on router R2 are receiving traffic normally and that Host-1 is correctly sending subscription messages to join the IPTV stream. Which action must the engineer take to correct the problem?
What is the difference between RPL and route-maps?
Refer to the exhibit.
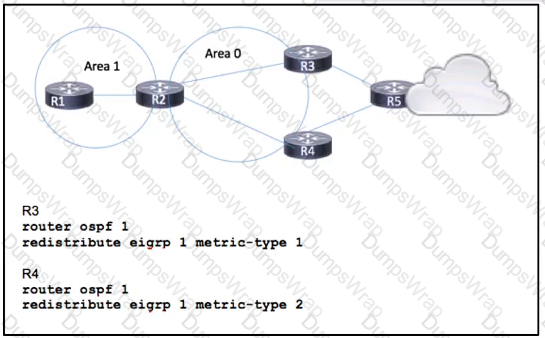
Routers R1, R2. R3, and R4 have been configured to run OSPF. and router R5 is running EIGRP Traffic from R1 to R5 is expected to pass via R4. but OSPF routing has calculated the best path via R3. Which action corrects the problem?
Refer to the exhibit.
After troubleshooting an OSPF adjacency issue, routers 1, 2, and 3 have formed OSPF
neighbor relationships. Which statement about the configuration is true?
Refer to the exhibit.
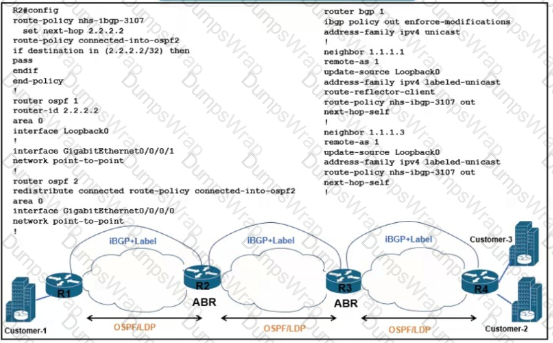
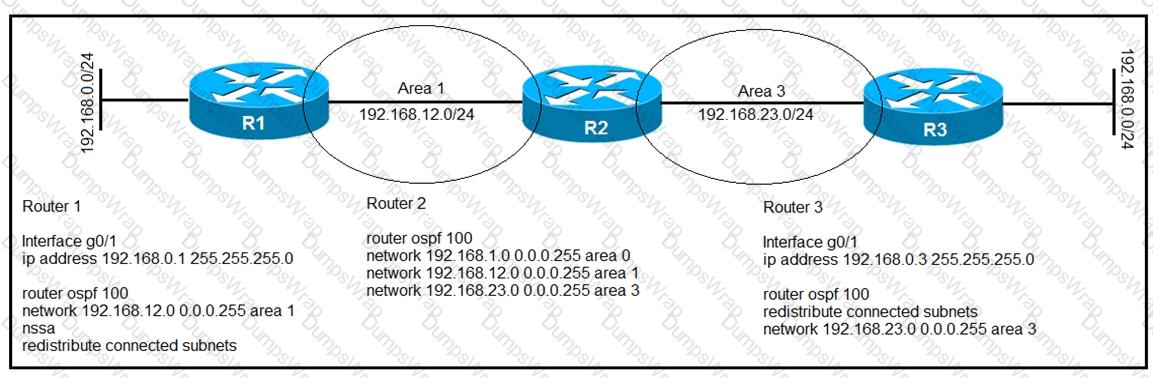
There is a connectivity issue between Customer-1 and Customer-2 File servers between the customers cannot send critical data R3 routes are missing from the routing table on the Customer-1 router All interlaces on Customer-1 are up Which configuration must be applied to router R2 to correct the problem?

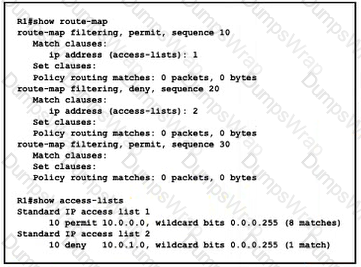
Refer to the exhibit A network engineer configured the redistribute connected subnets route-map filtering command on R1 to redistribute connected interfaces to the OSPF process The engineer also wants to filter out IP address 10 0 1 0/24. but the prefix still appears in the routing tables of the other routers on the network. Which action corrects the problem?
What is the role of a segment routing mapping server?
Refer to the exhibit.
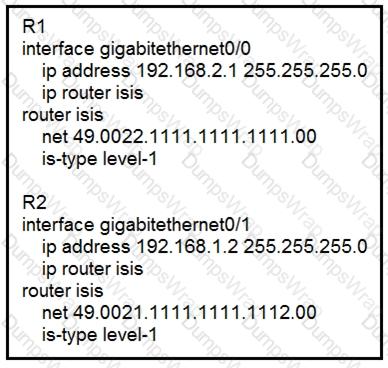
Routers R1 and R2 cannot form a neighbor relationship, but the network is otherwise
configured correctly and operating normally. Which two statements describe the problem? (Choose two.)
Which IPv6 prefix format defines the destination of a dynamic 6to4 tunnel?
In a PIM-SM environment, which mechanism determines the traffic that a receiver receives?
Refer to the exhibit.
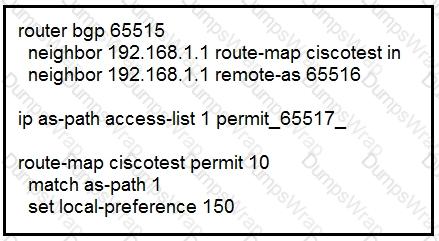
After troubleshooting BGP traffic steering issue, which action did the network operator
take to achieve the correct effect of this configuration?
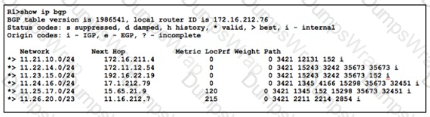
Refer to the exhibit. Company A established BGP sessions with several ISPs. A network engineer at the company must filter out all traffic except for routes that transit AS 152. The engineer configured the filtering policy “permit _152S_(_[0.9])” on R1, but after applying the configuration, the engineer notices that other routes are still visible. Which action resolves the issue?

Refer to the exhibit.
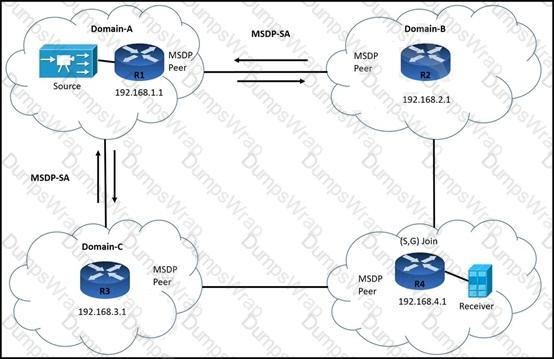
R3 is:
Which command must the engineer implement to resolve the issue?
A R3# ip msdp sa-filter in 192.168.3.1
B. R3# no ip msap sa-filter in 192.168.1.1
C R3# no ip msdp peer 192.168.1.1
D. R3# ip msdp sa-filter out 192.168.1.1
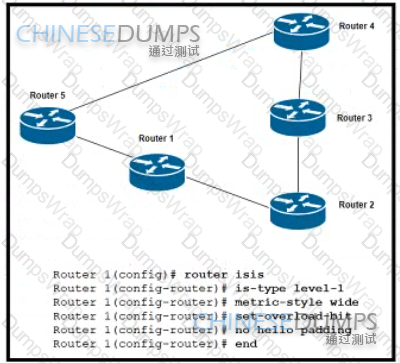
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer commissioned Router 1, which connects lo Router 2 and Router 5 Router 1 participates in IS-IS routing with other routers, but it is not used for transit traffic. Traffic from Router 2 to Router 5 is expected to travel via Router 1 but the traffic is travelog via Router 3 and Router 4 Which action reserves this problem?
An engineer is working to implement segment routing protocol on the customer's core network. Which step should the engineer take before the segment routing is enabled and is running with BGP?
Refer to the exhibit.

Router 1 and Router2 have shared routes in the OSPF database but the routes are missing from their routing tables. Checking me prefix-list configuration on both routers, the engineer confirmed all networks are allowed What action should the engineer take to fa the problem?
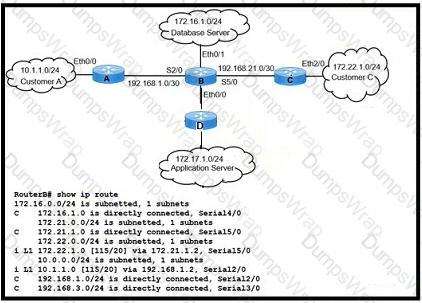
Refer to the exhibit. Customers A and C are experiencing packet drops when connecting to the application server While troubleshooting the problem the network engineer confirms that the IS-lS Level- 1/2 adjacency is up between routers A B C. and D and both customers can communicate with the database server without packet loss Which action must the engineer take to resolve the issue?

Refer to the exhibit. Company A established BGP sessions with several ISPs. A network engineer at the company must filter out all traffic except for routes that transit AS 152. The engineer configured the filtering policy “permit _152S_(_[0.9])” on R1, but after applying the configuration, the engineer notices that other routes are still visible. Which action resolves the issue?

Refer to the exhibit.
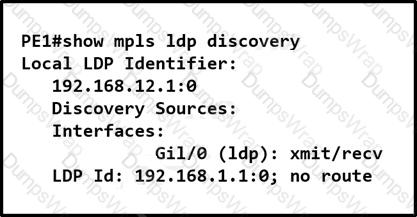
An administrator is troubleshooting network issues on a customer’s network PE1 cannot form an LDP relationship with PE2 using LDP ID 192 168.1.1. Due to this connectivity issue, the customer’s routes behind both PE routers cannot be exchanged. Which action must the administrator take to correct the problem?
For which reason can two devices fail to establish an OSPF neighbor relationship?
Which command is used to enable BIDIR-PIM under global configuration mode for Cisco IOS XE Sofware?
What is the purpose of a BGP confederation?
Refer to the exhibit.
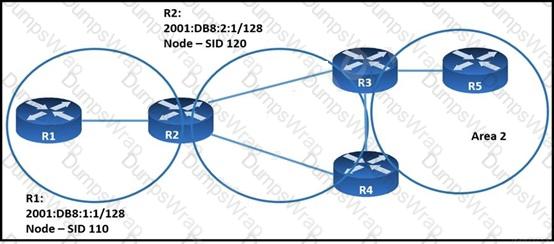
When implementing SRv6, which SID does R2 propagate into area 0 for the prefix 2001:DB8:1:1/128?
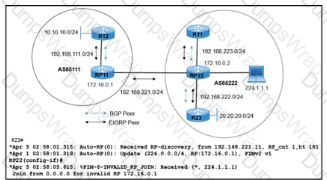
Refer to the exhibit. R21 is a multicast source sending multicast traffic 224.1.1.1 to R23, with RP22 serving as the rendezvous point inside AS65222. A network engineer noticed that when R21 goes down, R12 in AS65111 starts to send the same multicast group 224.1.1.1 through RP11. Which action resolves the issue ?
A network engineer is troubleshooting OSPF multiarea. Which Cisco IOS XR feature should the engineer use in order to streamline OSPF issue?
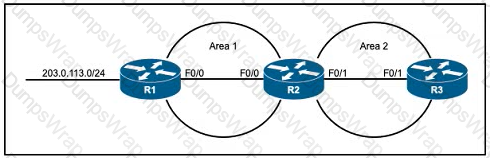
Refer to the exhibit After recent configuration changes to a customer's network, a network engineer notices that R2 cannot communicate with R3 Both FastEthemet interfaces on R2 and R3 are up and configured with the correct IP addresses MD5 password configured en R2 and R3 match with no issues What is the minimum change the engineer must make to enable R2 and R3 to communicate and fix the problem?
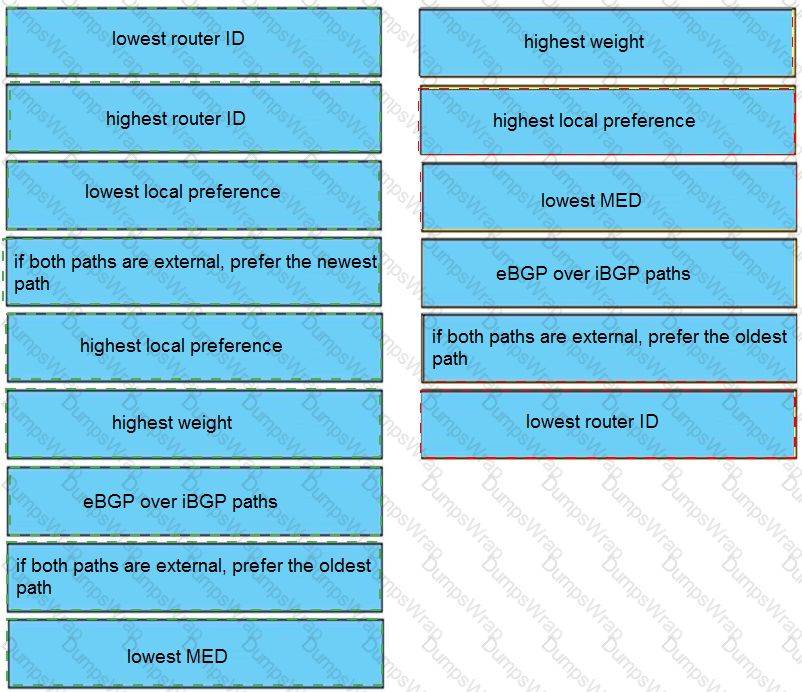
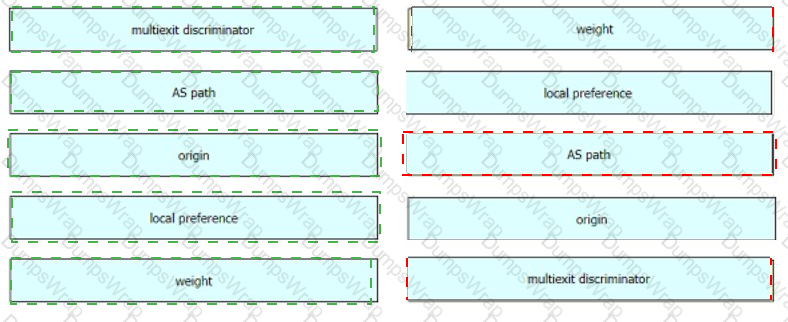
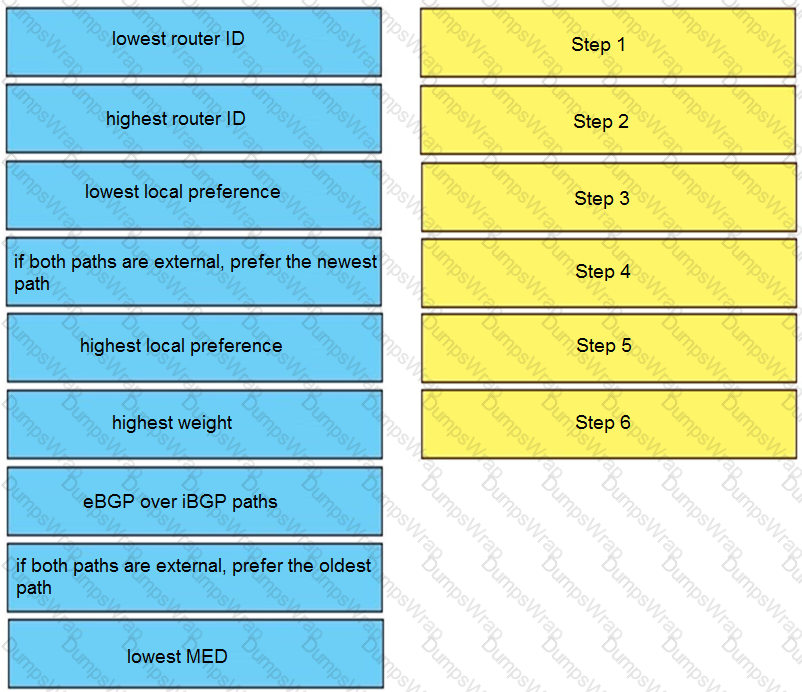
Drag and drop the attributes for the BGP route selection on the left into the correct order on the right. Not all options are used.
What is the difference between basic IS-IS and OSPF packet types?
Which feature provides service independence in service provider networks?
What is the difference between RPL and route-maps?
Refer to the exhibit.

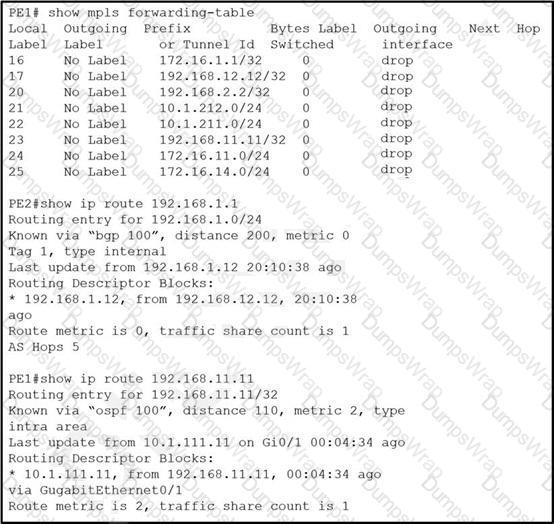
VPN users that are connected to PE routers are facing network issues. Traffic that originates from CE1 drops before reaching CE2. An engineer finds no outgoing traffic statistics on PE1 and PE2 routers toward CE devices and finds that the PE1 router is running the older software image. Which action must be implemented to resolve the issues?
Refer to the exhibit.
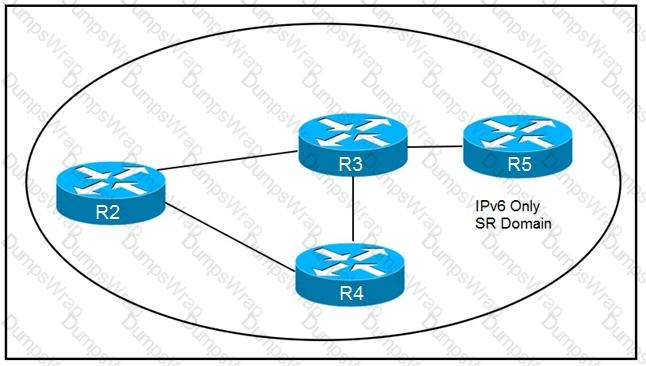
How are packets directed through the data plane when SRv6 is implemented?
Refer to the exhibit.
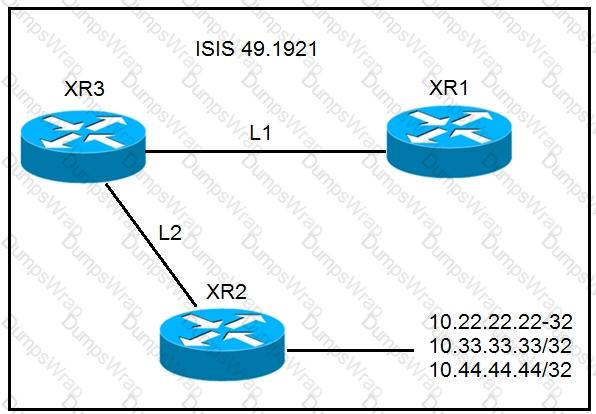
A network operator must stop 10.33.33.33/32 from being redistributed into Level 1 router
XR1. Which configuration meets this need?



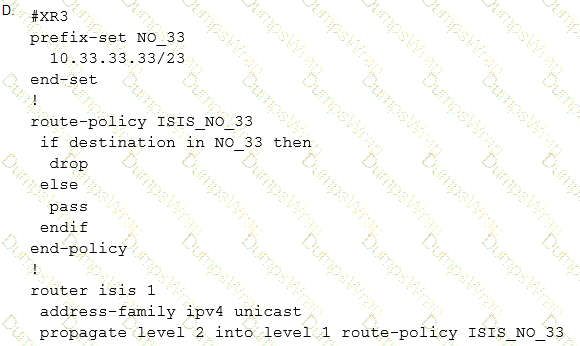
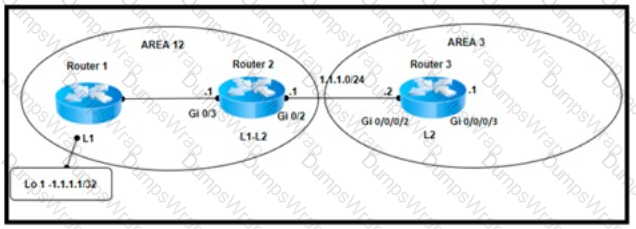
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer configured three new PE routers to expand the network. The new routers run in the IS-IS routing protocol and reside in the data center in the same exchange as the existing routers. However, the network is now experiencing suboptimal routing. The Layer 2 configuration and VLANs are configured correctly to provide segregation between networks, but the Level 1 routes are not being converted to Level 2 routes. Which action resolves the issue?
Refer to the exhibit.
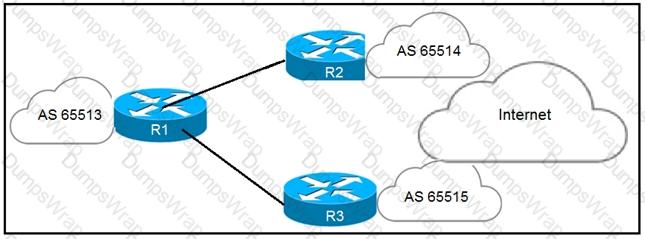
An engineer has successfully fixed BGP peering issue. R1 has an established eBGP
peering with R2 and R3. Which mechanism should the engineer apply in order to steer the traffic correctly?
Which two BGP route reflector attributes should be implemented to prevent routing loops? (Choose two)

Refer to the exhibit. The Cisco router has a single uplink to the upstream network, which is critical to the business. The router is configured for traffic steering with the Autoroute mechanism configured to steer all OSPF and IS-IS prefixes over non-shortest paths and divert traffic for those prefixes to the SR-TE policy. However, the Autoroute Announce functionality for all prefixes is not working. Which additional command set must the engineer configure on the router to correct this issue?

What are two features of dual-stack? (Choose two.)
Which keyword is used with the match route-type command to redistribute the external BGP and IGP routes using route map?
For which reason can two BGP peers fail to establish a neighbor relationship?
Refer to the exhibit.
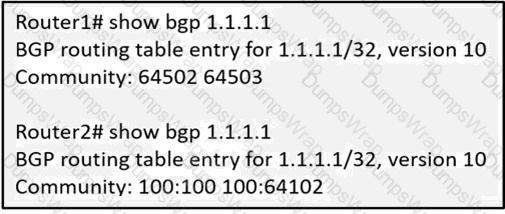
An engineer working on a client’s network is trying to solve the BGP community issue on R1 and R2 routers. After displaying the BGP entries, the engineer notices that both routers still have different outputs. Which action must the engineer perform to any of the routers to correct the problem and get the same output?
Refer to the exhibit.
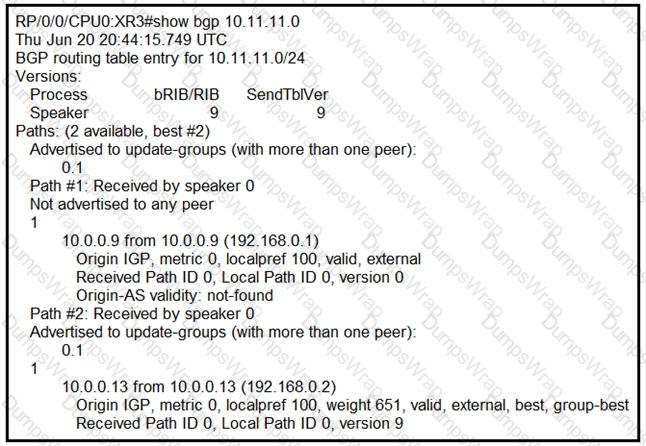
A network operator is getting the route for 10.11.11 0/24 from two upstream providers on
#XR3. The network operator must configure #XR3 to force the 10.11.11.0/24 prefix to route via next hop of 10.0.0.9 as primary when available. Which of these can the operator use the routing policy language for, to enforce this traffic forwarding path?
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is troubleshooting an OSPF issue. Router 1 has a neighbor relationship with
router 2. Only router 1 classful EIGRP routes can be seen on router 2. In order for all EIGRP routes to be redistributed correctly, which action should be taken?
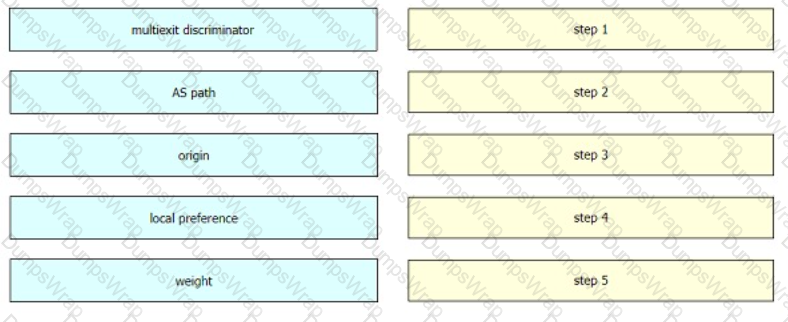
Drag and drop the BGP attributes from the left into the order of route selection preference on the right.
Which feature provides service independence in service provider networks?
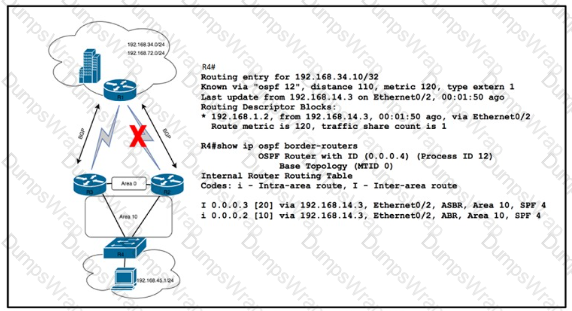
Refer to the exhibit. After a recent network implementation project, customer A is performing stress testing to verify network redundancy at the branch office connected to R4. When the link from R2 is shut öown as shown, the SLA tracking object fails and the cost of the link between R2 and R4 increases to 100. However, a traceroute operation from a PC in the Branch office shows that traffic to HQ is still routed via R2. Which solution corrects the problem and optimizes traffic flow via R3 without creating operational overhead?
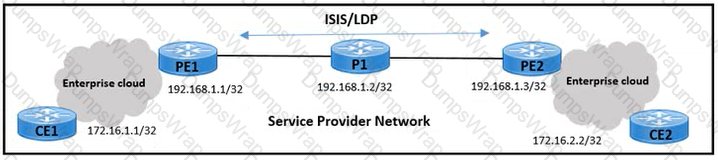
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer working for a private telecommunication company with an employee id 4115 46 881 is enabling a segment routing solution with these requirements.
- A service provider is using the default range for prefix SID.
- PE1 must allocate the first SID from the default range for the loopback address
- PE1 and PE2 loopback SID allocation should have a minimum difference of 500.
Which configuration must be implemented to meet the requirements?

Which two differences should be considered when deciding whether to implement to implement routing policies or route maps? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit.

Routers within the cluster are not receiving the desired prefixes. What must be done to fix the issue?
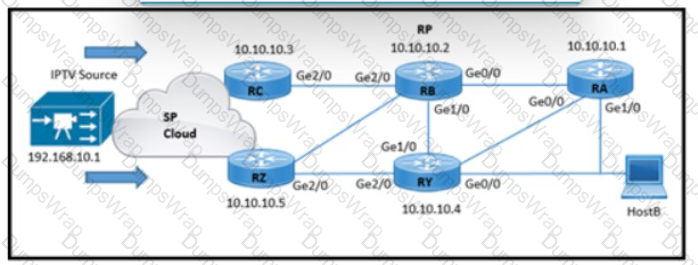
Refer to the exhibit. HostB receives an IPTV traffic stream from the multicast source at 192.168 10.1. When router RB is powered down, it impacts multicast traffic forwarding to downstream peers. The RA and RB routers reside in the same physical location. Which two configurations must be implemented so that HostB receives the multicast stream even when RB is powered down? (Choose two )
What are two differences between OSPF and IS-IS? (Choose two.)
What are two features of dual-stack? (Choose two.)
Refer to the exhibit.
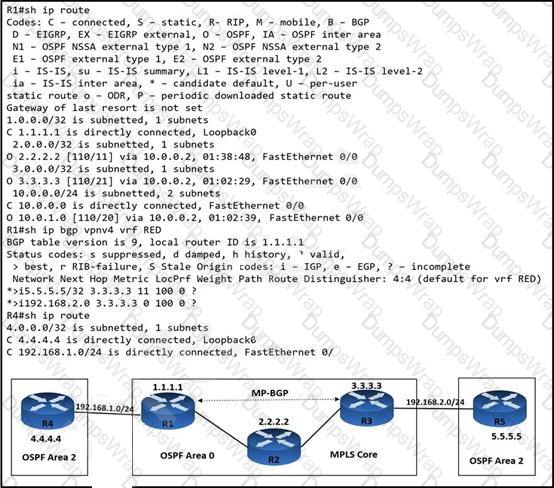
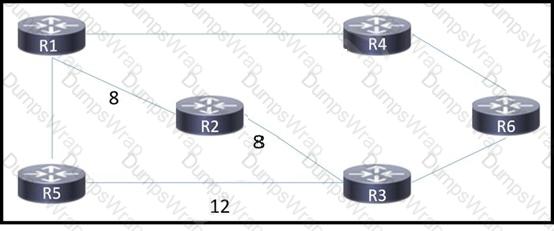
An engineer is troubleshooting connectivity issues on the MPLS core network. A customer connected through R4 cannot reach the OSPF domain on R5. While checking the routing table of R1, the engineer cannot see all the routes from R3 and R5. Which task must the engineer perform so that R4 is able to reach R5?