Google Certified Professional - Cloud Developer Questions and Answers
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
A recent security audit discovers that HipLocal’s database credentials for their Compute Engine-hosted MySQL databases are stored in plain text on persistent disks. HipLocal needs to reduce the risk of these credentials being stolen. What should they do?
For this question refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal wants to reduce the latency of their services for users in global locations. They have created read replicas of their database in locations where their users reside and configured their service to read traffic using those replicas. How should they further reduce latency for all database interactions with the least amount of effort?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
Which Google Cloud product addresses HipLocal’s business requirements for service level indicators and objectives?
HipLocal's.net-based auth service fails under intermittent load.
What should they do?
In order for HipLocal to store application state and meet their stated business requirements, which database service should they migrate to?
HipLocal's APIs are showing occasional failures, but they cannot find a pattern. They want to collect some
metrics to help them troubleshoot.
What should they do?
HipLocal wants to reduce the number of on-call engineers and eliminate manual scaling.
Which two services should they choose? (Choose two.)
Which database should HipLocal use for storing user activity?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
How should HipLocal redesign their architecture to ensure that the application scales to support a large increase in users?
Which service should HipLocal use for their public APIs?
Which service should HipLocal use to enable access to internal apps?
HipLocal has connected their Hadoop infrastructure to GCP using Cloud Interconnect in order to query data stored on persistent disks.
Which IP strategy should they use?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
How should HipLocal increase their API development speed while continuing to provide the QA team with a stable testing environment that meets feature requirements?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal is expanding into new locations. They must capture additional data each time the application is launched in a new European country. This is causing delays in the development process due to constant schema changes and a lack of environments for conducting testing on the application changes. How should they resolve the issue while meeting the business requirements?
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal's application uses Cloud Client Libraries to interact with Google Cloud. HipLocal needs to configure authentication and authorization in the Cloud Client Libraries to implement least privileged access for the application. What should they do?
HipLocal is configuring their access controls.
Which firewall configuration should they implement?
HipLocal’s data science team wants to analyze user reviews.
How should they prepare the data?
HipLocal wants to improve the resilience of their MySQL deployment, while also meeting their business and technical requirements.
Which configuration should they choose?
In order to meet their business requirements, how should HipLocal store their application state?
You need to migrate an internal file upload API with an enforced 500-MB file size limit to App Engine.
What should you do?
You are developing a microservice-based application that will run on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Some of the services need to access different Google Cloud APIs. How should you set up authentication of these services in the cluster following Google-recommended best practices? (Choose two.)
You are designing an application that uses a microservices architecture. You are planning to deploy the application in the cloud and on-premises. You want to make sure the application can scale up on demand and also use managed services as much as possible. What should you do?
You have an application deployed in Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) that reads and processes Pub/Sub messages. Each Pod handles a fixed number of messages per minute. The rate at which messages are published to the Pub/Sub topic varies considerably throughout the day and week, including occasional large batches of messages published at a single moment.
You want to scale your GKE Deployment to be able to process messages in a timely manner. What GKE feature should you use to automatically adapt your workload?
You are writing from a Go application to a Cloud Spanner database. You want to optimize your application’s performance using Google-recommended best practices. What should you do?
Your company has deployed a new API to App Engine Standard environment. During testing, the API is not behaving as expected. You want to monitor the application over time to diagnose the problem within the application code without redeploying the application.
Which tool should you use?
Your API backend is running on multiple cloud providers. You want to generate reports for the network latency of your API.
Which two steps should you take? (Choose two.)
Your application is controlled by a managed instance group. You want to share a large read-only data set
between all the instances in the managed instance group. You want to ensure that each instance can start
quickly and can access the data set via its filesystem with very low latency. You also want to minimize the total
cost of the solution.
What should you do?
Your company’s development teams want to use various open source operating systems in their Docker builds. When images are created in published containers in your company’s environment, you need to scan them for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs). The scanning process must not impact software development agility. You want to use managed services where possible. What should you do?
Your company stores their source code in a Cloud Source Repositories repository. Your company wants to build and test their code on each source code commit to the repository and requires a solution that is managed and has minimal operations overhead.
Which method should they use?
You are a developer working with the CI/CD team to troubleshoot a new feature that your team introduced. The CI/CD team used HashiCorp Packer to create a new Compute Engine image from your development branch. The image was successfully built, but is not booting up. You need to investigate the issue with the CI/CD team. What should you do?
You have an on-premises application that authenticates to the Cloud Storage API using a user-managed service account with a user-managed key. The application connects to Cloud Storage using Private Google Access over a Dedicated Interconnect link. You discover that requests from the application to access objects in the Cloud Storage bucket are failing with a 403 Permission Denied error code. What is the likely cause of this issue?
Your team develops stateless services that run on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). You need to deploy a new service that will only be accessed by other services running in the GKE cluster. The service will need to scale as quickly as possible to respond to changing load. What should you do?
Your website is deployed on Compute Engine. Your marketing team wants to test conversion rates between 3
different website designs.
Which approach should you use?
Your teammate has asked you to review the code below. Its purpose is to efficiently add a large number of small rows to a BigQuery table.

Which improvement should you suggest your teammate make?
You are a developer at a large organization. You are deploying a web application to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). The DevOps team has built a CI/CD pipeline that uses Cloud Deploy to deploy the application to Dev Test, and Prod clusters in GKE. After Cloud Deploy successfully deploys the application to the Dev cluster you want to automatically promote it to the Test Cluster. How should you configure this process following Google-recommended best practices?
You are a developer at a large corporation You manage three Google Kubernetes Engine clusters. Your team’s developers need to switch from one cluster to another regularly without losing access to their preferred development tools. You want to configure access to these clusters using the fewest number of steps while following Google-recommended best practices. What should you do?
You have deployed an HTTP(s) Load Balancer with the gcloud commands shown below.
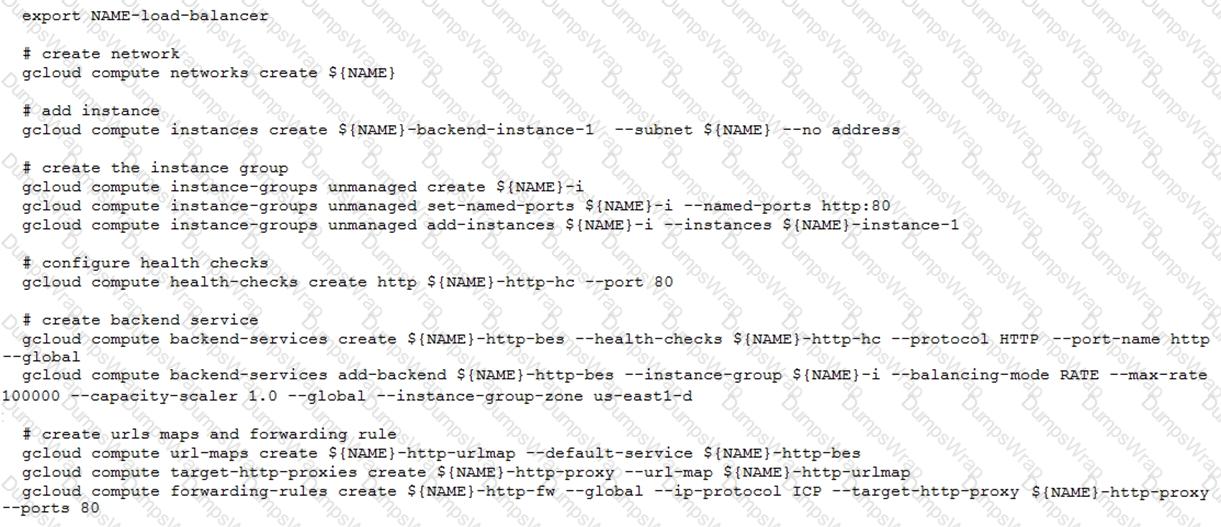
Health checks to port 80 on the Compute Engine virtual machine instance are failing and no traffic is sent to your instances. You want to resolve the problem.
Which commands should you run?
Your company has deployed a new API to a Compute Engine instance. During testing, the API is not behaving as expected. You want to monitor the application over 12 hours to diagnose the problem within the application code without redeploying the application. Which tool should you use?
Your development team has been asked to refactor an existing monolithic application into a set of composable microservices. Which design aspects should you implement for the new application? (Choose two.)
You are a SaaS provider deploying dedicated blogging software to customers in your Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. You want to configure a secure multi-tenant platform to ensure that each customer has access to only their own blog and can’t affect the workloads of other customers. What should you do?

