HCIA-Cloud Computing V5.5 Exam Questions and Answers
KVM is a type of paravirtualization. It can implement CPU and memory virtualization, but not device I/O virtualization.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
This statement isincorrectbased on HCIA–Cloud Computing virtualization concepts.
First,KVM is not a pure paravirtualization technology. It is ahardware-assisted full virtualizationsolution that relies on CPU virtualization extensions. While KVM can use paravirtualized drivers (such as Virtio) to improve performance, its core architecture is hardware-assisted virtualization.
Second, KVM supportsdevice I/O virtualization. Using technologies such asVirtio, KVM provides efficient virtual network and storage devices. This allows virtual machines to achieve near-native I/O performance, which is a key feature emphasized in HCIA training.
Because the statement incorrectly classifies KVM and wrongly claims that it cannot virtualize device I/O, the correct answer isFALSE.
Common storage networks include direct attached storage (DAS), network attached storage (NAS), and storage area network (SAN). SANs are divided into Fibre Channel storage area networks (FC SANs) and IP storage area networks (IP SANs).
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing technical guidelines, storage is categorized by its connection method and the protocol used to access data. Direct Attached Storage (DAS) is the most basic form, where storage devices are connected directly to a single server via an internal bus or external cable. While simple, it lacks the scalability and resource-sharing capabilities required for modern cloud data centers. Network Attached Storage (NAS) provides file-level access over a standard IP network, typically using protocols like NFS or CIFS, allowing multiple clients to share a central pool of files over a local area network.
The Storage Area Network (SAN) is a specialized, high-speed network that provides block-level access to storage, making it appear to the operating system as a locally attached disk. In Huawei’s virtualization solutions, SANs are the preferred choice for high-performance clusters and features like VM Live Migration. As the statement correctly identifies, SANs are primarily divided into two types based on the transport protocol used: Fibre Channel (FC) SANs and IP SANs. FC SANs utilize dedicated fiber-optic cables, FC switches, and Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) to transmit data using the Fibre Channel protocol, offering extremely high reliability and minimal latency. Conversely, IP SANs utilize standard Ethernet infrastructure and the iSCSI protocol to encapsulate SCSI commands into IP packets. This allows for lower costs and easier management by leveraging existing Ethernet knowledge. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for the HCIA exam, as the choice between FC and IP SAN directly impacts the deployment architecture and performance characteristics of Huawei's FusionCompute and FusionAccess solutions in an enterprise environment.
Enterprise administrators provision virtual desktops and perform routine maintenance through virtual desktop service management. Which of the following are the provisioning proportion modes of preset virtual desktops in desktop provisioning management?
Options:
1:1
1:N
1+1
M:N
Answer:
A, BExplanation:
In the Huawei FusionAccess solution, desktop provisioning is the process of creating and assigning virtual machines to users. The "provisioning proportion mode" is a key parameter in this process. Mode A (1:1) represents the "Single User" or "Static" assignment mode. In this configuration, one virtual machine is permanently bound to one user. This is typically used for Full Copy desktops where the user requires a persistent environment with their own dedicated storage and personalized settings. The user has exclusive rights to the VM, and their data remains on the disk even after logging off. This ensures the highest level of personalization and performance for individual employees.
Mode B (1:N) represents the "Dynamic" or "Pool" assignment mode. In a 1:N scenario, a group of users shares a pool of virtual machines. This is commonly implemented using Linked Clone technology to save storage space and simplify management. For example, in a task-oriented environment like a call center or a training center, multiple users (N) can log into a set of virtual machines based on the same template (1) at different times. The system assigns an available VM from the pool to the user upon login. This maximizes resource utilization because not all users are online simultaneously.
Furthermore, the selection of these modes directly affects the backend storage design and the maintenance strategy. For 1:1 desktops, backup and disaster recovery must be managed per individual VM, whereas for 1:N pooled desktops, the administrator focuses on the security and integrity of the "Golden Image" or parent template. Understanding these two primary modes is crucial for administrators to choose the right technology—Full Copy for persistent 1:1 needs or Linked Clone for efficient 1:N pools—based on user requirements and hardware capacity.
====================
Which of the following statements istrueabout the FusionCompute storage architecture?
Options:
Physical storage media that deliver storage space for virtualization are called storage devices.
LUNs allocated by Huawei Distributed Storage can be encapsulated as datastores.
After storage resources are converted to datastores and associated with hosts, virtual disks can be created for VMs.
FusionCompute uniformly encapsulates storage units of storage resources into datastores.
Answer:
DExplanation:
FusionCompute uses aunified storage abstraction model. Regardless of whether the backend storage is SAN, NAS, local disks, or distributed storage, FusionComputeencapsulates storage resources into datastores.
This abstraction simplifies management and allows virtual machines to consume storage in a standardized manner. While statements A, B, and C describe correct individual concepts,D best represents the core architectural principleemphasized in HCIA documentation.
Therefore, the correct answer isD.
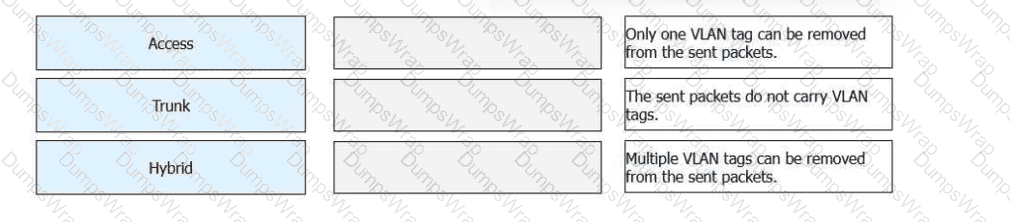
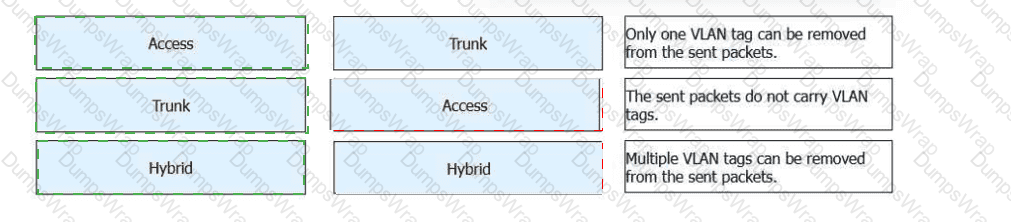
Match the following VLAN interface types with their descriptions.
Options:
Answer:
Explanation:
Access Interface
➡The sent packets do not carry VLAN tags.
An access interface belongs to only one VLAN.
Frames are sent untagged, making it suitable for end devices such as PCs and printers.
Trunk Interface
➡Only one VLAN tag can be removed from the sent packets.
A trunk interface allows multiple VLANs to pass.
Typically used for switch-to-switch connections.
Only the native VLAN is sent untagged; other VLANs are tagged.
Hybrid Interface
➡Multiple VLAN tags can be removed from the sent packets.
A hybrid interface supports both tagged and untagged VLAN traffic.
Multiple VLANs can be configured to send traffic without VLAN tags.
Commonly used for server connections and virtualization environments.
Which of the following commands are used to view common files on Linux?
Options:
less
more
vim
cat
Answer:
A, B, DExplanation:
In the HCIA–Cloud Computing syllabus, Linux command-line operations are part of theOperating System Basicsdomain. Viewing file contents is one of the most common Linux administration tasks.
Theless (A)command is used to view file contents page by page. It supports forward and backward scrolling and searching, making it suitable for viewing large files. HCIA materials often recommend less as a preferred file-viewing tool.
Themore (B)command is an earlier paging command that displays file contents one screen at a time. Although it has fewer features than less, it is still a valid file-viewing command.
Thecat (D)command is used to display the entire content of a file directly to standard output. It is commonly used for viewing small files or concatenating files.
Thevim (C)command is primarily atext editor, not a file-viewing command. While it can open and display files, its main purpose is editing rather than viewing, which is how HCIA differentiates it.
Therefore, the correct answers areA, B, and D.
Which of the following statements aretrueabout deploying Compute Node Agent (CNA) and Virtual Resource Management (VRM) in Huawei FusionCompute?
Options:
CNA can be deployed on virtual machines or physical servers.
If the VRM nodes are deployed on physical servers, the active and standby VRM nodes must be deployed on two physical servers.
If the VRM nodes are deployed on virtual machines, you need to select two hosts in the management cluster and deploy the active and standby VRM VMs on these hosts.
VRM can be deployed on virtual machines or physical servers.
Answer:
B, C, DExplanation:
In FusionCompute architecture,CNAandVRMhave clearly defined deployment models.
OptionAis false.CNA is deployed only on physical servers(compute nodes). It is responsible for interacting directly with hardware resources and cannot run inside a VM.
OptionBis true. When VRM is deployed on physical servers,active and standby VRM nodes must be installed on separate physical serversto ensure high availability.
OptionCis true. When VRM is deployed on virtual machines, the active and standby VRM VMs must be placed ondifferent hosts within the management clusterto avoid single points of failure.
OptionDis true. VRM supports deployment oneither physical servers or virtual machines, providing flexible management options.
Therefore, the correct answers areB, C, and D.
Which of the following statements aboutservice adjustmentin FusionAccess aretrue?
Options:
A computer whose assignment type isAssign a Computer to Multiple UsersorAssign Computers to a Desktop Groupcannot be assigned again after being unassigned.
If a computer whose assignment type isAssign a Computer to a Useris unassigned and then assigned again, the computer automatically starts. After the virtual desktop icon on the WI turns on, wait about three minutes and then log in.
If a computer whose assignment type isAssign a Computer to a Useris unassigned and then assigned again, the computer can only be assigned to the original user and cannot be assigned to other users.
A computer whose assignment type isAssign a Computer to a Useris automatically shut down after being unassigned.
Answer:
B, DExplanation:
FusionAccess defines clear behaviors for desktop service adjustment:
Bis true. After reassignment, the systemautomatically starts the desktop, and a short wait time is required before user login.
Dis true. When a desktop assigned to a single user is unassigned, the systemautomatically shuts it downto save resources.
Ais false. Desktops assigned to multiple users or desktop groupscan be reassignedafter being unassigned.
Cis false. After unassignment, a desktop can beassigned to a different user, not only the original one.
Thus, the correct answers areB and D.
Which of the following statements is false about the Libvirt component?
Options:
Both KVM and Xen can invoke APIs provided by Libvirt to manage virtualization platforms.
Libvirt provides programming interfaces in multiple languages. You can directly invoke APIs provided by Libvirt to perform operations on VMs.
Libvirt is a set of library functions that are invoked by other technologies to manage VMs on servers.
Libvirt is a closed-source project. It is a very powerful management tool.
Answer:
DExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum regarding Open Source Virtualization, statement D is FALSE. Libvirt is famously an open-source toolkit and API, licensed under the LGPL. It was specifically designed to provide a stable, long-term abstraction layer for managing different virtualization technologies. It is not a proprietary or "closed-source" product. In fact, its open nature is what allowed it to become the industry standard for managing Linux-based hypervisors.
The other statements accurately describe Libvirt's role in a cloud environment. As noted in statement A, Libvirt is "hypervisor-agnostic," meaning it can manage multiple types of virtualization, including KVM, Xen, QEMU, and even LXC containers. This allows management tools to use a single set of commands regardless of the underlying technology. Statement B is correct because Libvirt provides bindings for numerous programming languages, such as Python, C, and Java, enabling developers to automate VM lifecycle management (start, stop, migrate, snapshot) directly through code. Statement C is also true; Libvirt is essentially a collection of library functions and a daemon (libvirtd) that higher-level management platforms, such as Huawei'sFusionComputeor the open-sourceOpenStack, invoke to communicate with the hardware.
In Huawei's virtualization architecture, Libvirt acts as a crucial middle layer. By using the virsh command-line tool (which is part of the Libvirt package), administrators can perform complex VM operations without needing to understand the specific, low-level command syntax of each different hypervisor. Understanding that Libvirt is open-source and provides this universal management interface is a key learning point for the HCIA exam.
====================
Which of the following statements about the differences between a domain and an OU are true?
Options:
Users can log in to a domain but not to an OU.
Group policies can be configured for both OUs and domains.
An OU can exist in a domain, and a domain can also exist in an OU.
Both OUs and domains can contain AD objects.
Answer:
A, B, DExplanation:
In the context of FusionAccess deployment, understanding Microsoft Active Directory (AD) is critical. According to the official Huawei curriculum, a Domain and an Organizational Unit (OU) serve different purposes in a network hierarchy. Statement A is TRUE because a domain is a security and administrative boundary; users authenticate "to the domain." An OU is merely a logical container inside that domain used for organization; it does not function as an authentication boundary itself.
Statement B isTRUE. Group Policy Objects (GPOs) are the primary tool for managing desktop settings in a Huawei VDI environment. GPOs can be linked at the Domain level (applying to everyone) or at the OU level (applying only to the users or computers within that specific folder). This allows FusionAccess administrators to apply specific security rules—such as disabling USB ports or setting custom wallpapers—to one department (one OU) without affecting the entire company.
Statement D is alsoTRUE. Both entities are containers for AD objects such as User accounts, Computer accounts, and Security Groups. However, statement C isFALSE. While an OU always existsinsidea domain (to organize that domain's objects), a domaincannotexist inside an OU. Domains exist within a Forest or Tree structure.2This distinction is vital for HCIA candidates because the FusionAccessITA (IT Adapter)requires a specific OU structure to be pre-created (e.g., an OU for Desktops and an OU for Users) to properly apply the automated provisioning and management policies that define the desktop cloud environment.
====================
A router manages path information by managing its___
Options:
Answer:
Routing Table
Explanation:
As defined in the "Network Technology Basics" module of the HCIA-Cloud Computing training, a router is a Layer 3 (Network Layer) device responsible for interconnecting different network segments and selecting the optimal path for data packets. To perform this function, the router maintains and manages a Routing Table. This table is the "map" of the network that the router uses to make forwarding decisions. Every entry in the routing table typically includes several key parameters: the destination network address, the subnet mask, the protocol (how the route was learned, such as Static, OSPF, or BGP), the preference value, the cost (metric), and the next-hop address or outbound interface.
When a router receives an IP packet, it examines the destination IP address and performs a lookup in its routing table to find the most specific match (longest match rule). If a matching entry is found, the router encapsulates the packet into a new frame and sends it toward the next hop. If no match is found and no default route exists, the packet is discarded. This process is fundamental to the operation of a Cloud Data Center where multiple Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and subnets must communicate through virtual or physical routers.
While a switch manages a MAC address table to forward frames at Layer 2, and a host manages an ARP table to map IP addresses to MAC addresses, only the routing table provides the cross-network path intelligence required for routing. In Huawei’s virtualization solutions, virtual routers within the software-defined networking (SDN) layer use these same logic principles to ensure that traffic between virtual machines in different subnets is directed efficiently to the correct destination. Proper management of the routing table is therefore the cornerstone of network reachability in cloud environments.
====================
During FusionAccess virtual desktop provisioning, when a VM is being created, which of the following components checks whether the specified VM group and desktop group exist?
Options:
HDC
GaussDB
HDA
HDP
Answer:
AExplanation:
In FusionAccess architecture:
HDC (Huawei Desktop Controller) is responsible for desktop lifecycle management, including provisioning logic, policy enforcement, and resource validation.
During VM creation, HDC verifies whether the specified VM group and desktop group exist and whether configurations are valid.
Other components:
GaussDB stores metadata.
HDA runs inside desktops.
HDP is a display protocol.
Thus, the correct answer is HDC.
Which of the following statements aretrueabout the features and functions of the FusionCompute virtualization suite?
Options:
Allowing users to add or reduce VM resources on demand without interrupting applications.
Supporting x86- or Arm-based servers, various storage devices, and mainstream Linux/Windows operating systems, thereby allowing mainstream applications to run on virtualization platforms.
Allowing users to define service level agreement (SLA) policies to control VM resources, thereby allocating physical resources based on application priority.
Automatically migrating workloads based on preset policies, thereby optimizing resource allocation, system response efficiency, and user experience.
Answer:
A, B, C, DExplanation:
Huawei FusionCompute provides a comprehensive virtualization platform with advanced management and scheduling capabilities.
Ais true. FusionCompute supportsdynamic resource adjustment, including CPU and memory scaling, helping applications adapt to workload changes.
Bis true. FusionCompute supportsx86 and Arm architectures, multiple storage backends, and mainstream operating systems such as Linux and Windows, ensuring broad application compatibility.
Cis true. SLA policies allow administrators to define priorities for virtual machines, ensuring that critical applications receive sufficient resources.
Dis true. FusionCompute supportsautomatic VM migration (such as DRS-like features)based on predefined policies to balance workloads and optimize system performance.
All listed statements correctly describe FusionCompute capabilities.
Cloud-native technologies enable organizations to build and run scalable applications in public, private, or hybrid cloud environments. Which of the following isnota representative cloud-native technology?
Options:
Service mesh
Virtualization
Microservice
Container
Answer:
BExplanation:
Cloud-native architecture emphasizesapplication-level design and management, focusing on agility, scalability, and resilience.
Microservices,containers, andservice meshesare core cloud-native technologies.
Virtualizationis a foundational cloud technology but belongs totraditional cloud infrastructure, not cloud-native application architecture.
Therefore, the correct answer isVirtualization.
Which of the following storage types isrecommendedfor VRM deployment during Huawei FusionCompute installation?
Options:
IP SAN
FC SAN
Local storage
NAS
Answer:
CExplanation:
According to the HCIA–Cloud Computing documentation forFusionCompute installation, theVirtual Resource Management (VRM)node plays a critical role in managing virtualization resources such as hosts, virtual machines, and clusters.
Huawei recommends deploying theVRM system disk on local storage. The main reasons are reliability and independence. Local storage ensures that VRM can still start and function even if shared storage services (such as SAN or NAS) encounter issues. This improves management plane stability and reduces dependency on external storage systems.
Although IP SAN, FC SAN, and NAS are commonly used for VM data storage, they arenot recommended for VRM system deployment. HCIA materials clearly emphasize that VRM should rely onlocal disksto guarantee management availability.
Therefore, the correct answer isLocal storage.
Hypervisor is the key to virtualize compute resources.7Which of the following is also called a hypervisor?
Options:
VPM
VRM
VNM
VMM
Answer:
DExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing technical documentation, the term Hypervisor is used interchangeably with Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM). The VMM is the core software component that creates the virtualization layer between the physical hardware and the Guest Operating Systems. Its primary responsibility is to abstract physical resources (CPU, Memory, I/O) and present them as logical, virtualized resources to the Virtual Machines. The VMM manages the execution of the Guest OS and ensures that different VMs remain isolated from one another on the same physical host.8
In the Huawei ecosystem, specifically within theFusionComputearchitecture, the hypervisor functionality is provided by theCNA (Computing Node Agent)node using the UVP (Universal Virtualization Platform) engine.9While "Hypervisor" is a general industry term, "VMM" specifically describes the role of monitoring and mediating the hardware requests from virtualized guests.10The other options provided are incorrect in this context:VRM (Virtual Resource Management)is the centralized management node that coordinates multiple CNA nodes but is not the hypervisor itself.VNA (Virtual Node Agent)is an agent running on the CNA node that communicates with the VRM, but it does not perform the actual hardware virtualization.
The VMM performs critical tasks such as instruction trapping and emulation.11When a Guest OS attempts to execute a "privileged instruction" that would normally interact directly with the hardware, the VMM intercepts it and executes it safely on behalf of the VM.12This ensures that a single VM cannot crash the entire physical host or access the data of another VM. Understanding that the Hypervisor and VMM are the same entity is fundamental to mastering the taxonomy of virtualization used in Huawei's ICT training and exams.
====================
A bare VM is required when creating a virtual desktop template on FusionAccess. Which of the following statements aretrueabout creating a bare VM?
Options:
TheConfiguration Modeof the system disk must be set toCommon.
NICs cannot be added when creating a linked-clone bare VM, but NICs can be added when the linked-clone template is used for quick provisioning.
The NIC can be the service-plane distributed virtual switch (DVS) and port group of the user VM.
TheConfiguration Modeof the system disk must be set toThin provisioning.
Answer:
A, BExplanation:
Bare VM creation rules in FusionAccess are strict to ensuretemplate consistency and successful provisioning:
Ais true: The system disk must useCommon configuration mode, not thin provisioning.
Bis true: For linked-clone bare VMs, NICs are addedafter template creation, during desktop provisioning.
Cis false: Bare VMs should usemanagement-plane networking, not user service-plane DVS/port groups.
Dis false: Thin provisioning isnot allowedfor the system disk of a bare VM.
Therefore, the correct answers areA and B.
In FusionCompute, which of the following isnota prerequisite for VM live migration?
Options:
The VM must be in the running state.
The uplink of the distributed virtual switch (DVS) where the VM NIC resides must be associated with both the source and target hosts.
The IMC policy of the cluster must be configured.
The datastore to which the VM disk belongs must be associated with both the source and target hosts.
Answer:
CExplanation:
VM live migration in FusionCompute has several mandatory prerequisites.
Ais required because live migration applies only torunning VMs.
Bis required to ensure uninterrupted network connectivity during migration.
Dis required because both source and target hosts must access the same datastore to migrate VM disks seamlessly.
IMC policy (C)isnot mandatoryfor live migration. It is requiredonly when hosts have different CPU models. If hosts use compatible CPUs, live migration can proceed without configuring IMC.
Therefore, the correct answer isC.
Programs and data must be loaded into memory for CPU processing, and then be placed on external storage for long-term preservation.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
The statement describes the fundamental operation of the Von Neumann architecture, which serves as the core foundation for modern server hardware used in cloud computing environments. In the official Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, specifically under the "Server Basics" module, the distinction between volatile and non-volatile storage is emphasized as a critical hardware concept. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) acts as the primary compute engine but cannot execute instructions directly from secondary storage devices, such as Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) or Solid State Drives (SSDs), due to the massive latency gap between CPU clock speeds and disk access times.
Therefore, for any task to be performed, the relevant programs and data must first be loaded into the system memory, or Random Access Memory (RAM). RAM provides the high-speed, low-latency access required for the CPU to fetch and execute instructions efficiently. However, RAM is volatile, meaning all stored data is lost when the power supply is interrupted. To ensure long-term preservation and data persistence, processed results or saved files must be written back to external or secondary storage. These storage devices are non-volatile and provide the capacity needed to store operating systems, applications, and user data across reboots. In a cloud environment, such as one utilizing Huawei FusionServer Pro, this cycle of data movement between storage and memory is critical for maintaining system performance. The memory acts as a high-speed buffer for active tasks, while the storage provides the persistent layer. Understanding this hardware interaction is vital for cloud administrators because virtualization performance often hinges on the balance between memory capacity and storage I/O throughput.
====================
Which of the following statements is false about concepts of virtualization?
Options:
A guest OS is the OS running on a virtual machine (VM).
A host machine is a physical machine.
A host OS is the virtualization software layer.
A guest machine is a VM.
Answer:
CExplanation:
In the "Virtualization Basics" section of the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training material, the taxonomy of virtualization components is strictly defined. Statement C is FALSE because the virtualization software layer is technically called the Hypervisor or Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), not the "Host OS." While a "Host OS" exists in Type-2 (hosted) virtualization (where the hypervisor runs as an application on top of an existing OS like Windows or Linux), the software layer that actually performs the resource abstraction and logical partitioning is the Hypervisor itself.
The other definitions are central to Huawei's technical documentation. AGuest OS(Statement A) is indeed the operating system—such as Windows Server or Ubuntu—that is installed inside a Virtual Machine. It is "unaware" that it is running on virtual hardware. TheHost Machine(Statement B) refers to the underlying physical server (e.g., a Huawei FusionServer Pro) that provides the actual CPU, RAM, and physical NICs. Finally, aGuest Machine(Statement D) is a synonym for a Virtual Machine (VM), representing the logical container that houses the Guest OS and applications.
In a Type-1 virtualization architecture (like HuaweiFusionCompute), the Hypervisor (CNA) sits directly on the hardware. In this scenario, there is no "Host OS" at all, further proving why statement C is incorrect. The Hypervisor is responsible for trapping "privileged instructions" from the Guest OS and translating them into actions on the physical hardware. Correctly identifying these roles—Host Machine, Hypervisor, and Guest VM—is a prerequisite for understanding more advanced cloud features like Resource Clusters and Distributed Resource Scheduling (DRS).
In the OpenStack solution,Swiftprovides persistent block storage.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
In OpenStack:
Swiftprovidesobject storage, designed for storing unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups.
Cinderprovidesblock storage, which is used by virtual machines as virtual disks.
Since Swift doesnotprovide block storage, the statement isFALSE.
Which of the following statements about the differences betweenuser groupsandorganizational units (OUs)aretrue?
Options:
OUs and user groups are Active Directory objects.
An OU can contain objects such as accounts, computers, printers, and shared folders.
Group policies can be configured for both OUs and user groups.
A user group can only contain accounts.
Answer:
A, BExplanation:
In AD,OUsanduser groupsare both used for organizing and managing resources, but they differ in function.
Ais true. Both OUs and user groups areAD objects.
Bis true. An OU can contain multiple types of AD objects, includingusers, computers, printers, and shared resources.
Cis false.Group policies cannot be directly applied to user groups; they are applied to domains, sites, or OUs.
Dis false. A user group can containusers, computers, and even other groups, not only user accounts.
Thus, the correct answers areA and B.
Which of the following FusionAccess componentsdoes not have backup data?
Options:
License
WI
VLB
vAG
Answer:
AExplanation:
FusionAccess consists of multiple components, each with different roles and data persistence requirements.
WI (Web Interface)stores configuration and user access information and supports backup.
VLB (Virtual Load Balancer)maintains configuration data that can be backed up.
vAG (Virtual Access Gateway)also stores configuration-related data that supports backup and recovery.
TheLicensecomponent, however, isnot backed upas configuration or system data. Licensing information is typically re-imported or reactivated during recovery rather than restored from backup.
Therefore, the component that doesnothave backup data isLicense.
Which of the following statements is false about virtualized storage?
Options:
LUNs allocated by Huawei Distributed Block Storage can be encapsulated as data stores.
Storage virtualization abstracts storage devices to a data store so that each VM can be stored as a group of files in a directory on the data store.
A data store is a logical repository that is similar to a file system. It combines storage devices of different types and provides a unified model to store VM files.
Storage virtualization greatly improves storage resource utilization.
Answer:
CExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, statement C is FALSE regarding the architecture of a datastore. While a datastore is indeed a logical repository similar to a file system, it does not "combine storage devices of different types" into a single unified model. In FusionCompute, a datastore has a strict 1-to-1 relationship with its underlying storage resource. For example, a datastore created on an FC SAN LUN is separate from a datastore created on an NFS share or a local disk. You cannot merge a LUN from a SAN and a folder from a NAS into a single "Datastore" entity. Each datastore is formatted with a specific file system (like VIMS for block storage or NFS for file storage) that is native to that specific storage type.
The other statements represent the core principles of storage virtualization in the Huawei ecosystem. Statement A is true; LUNs from Huawei's distributed block storage (FusionStorage) are presented to hosts as block devices and can then be initialized as VIMS datastores. Statement B is a fundamental definition ofVirtualized Storage: the hypervisor uses a cluster file system (VIMS) to hide the complexities of the hardware, allowing each VM to exist simply as a set of files (configuration files, disk files like .vhd, and log files) inside a directory.
Statement D is also correct; storage virtualization significantly improves utilization through technologies likeThin Provisioning. In a traditional environment, if you allocate 100GB to a server, that space is "locked." In a virtualized environment with thin provisioning, the datastore only consumes the actual physical space being used by the data, allowing administrators to "over-allocate" storage and maximize the efficiency of their physical disk arrays.
Which of the following statements are true about system encapsulation and Sysprep (system encapsulation tool) for creating a full copy template on FusionAccess?
Options:
Sysprep can delete specific system information from an installed Windows image.
Sysprep can be used to reset Windows product activation.
System encapsulation can complete system installation in minutes.
During system encapsulation, you cannot add software to the system.
Answer:
A, BExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training material, system encapsulation is a vital process when creating a "Golden Image" for Full Copy virtual desktops. The primary tool used for this in Windows environments is Sysprep (System Preparation Tool). Statement A is TRUE because the fundamental purpose of Sysprep is to "generalize" the operating system. This process removes computer-specific information, such as the Security Identifier (SID), computer name, and specific hardware drivers. If multiple VMs were cloned from a template without this step, they would all share the same SID, leading to domain conflict issues and security vulnerabilities in an enterprise Active Directory environment.
Statement B is alsoTRUE. Sysprep includes a functionality to reset the Windows Product Activation clock (often referred to as a "rearm"). This allows the cloned virtual machines to start their grace period anew upon their first boot, which is essential for large-scale deployments before the KMS (Key Management Service) or other volume licensing activation takes place. Statement C is incorrect because encapsulation is the process of preparing an image, not the installation itself; while cloning from a template saves time, "encapsulation" does not perform the installation. Statement D is incorrect because administrators typically install all necessary service software and driversbeforeor during the Audit Mode phase of Sysprep to ensure the final template is fully equipped.
In the Huawei FusionAccess workflow, encapsulation is the penultimate step before converting the VM into a template. By stripping the uniqueness of the source VM, Sysprep ensures that every Full Copy desktop provisioned to an end-user starts as a clean, unique instance that can successfully join the corporate domain and receive independent security policies.
====================
In Huawei FusionCompute, a VM running Linux is created. In this scenario, which of the following does the guest OS run in?
Options:
VRM
CNA
Linux VM
VNA
Answer:
CExplanation:
(Note: The original question contained a typo. As requested, "host OS" has been corrected to "guest OS" because Linux, in this scenario, is the Guest operating system.)
In the official Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum, the architecture of a virtualized system is divided into the Host Machine and the Guest Machine. TheHost Machineis the physical server (hardware) and the virtualization software (CNA in FusionCompute). TheGuest Machineis the Virtual Machine (VM) created by the hypervisor. According to the training materials, theGuest OSis the operating system that is installed and executed within the virtualized environment of a VM.13
Therefore, if a VM running Linux is created, the Linux operating system is the Guest OS, and it runs specifically inside theLinux VM. The VM acts as a logical container that provides the Linux OS with virtualized CPU, memory, storage, and network resources.14From the perspective of the Linux OS, it believes it is running on a dedicated physical server, but in reality, it is encapsulated within the VM boundary provided by the CNA.
The other components mentioned have different roles:CNA (Computing Node Agent)is the "host" software that manages the hardware and hosts the VM, but the Linux OS does not run "in" the CNA directly; it runs in the VM managed by the CNA.VRM (Virtual Resource Management)is the management platform used by administrators to create and configure the VM.VNA (Virtual Node Agent)is a process within the CNA that handles management commands from the VRM. In the Huawei certification logic, it is crucial to distinguish between the "Container" (the VM) and the "Occupant" (the Guest OS). The Guest OS is always tied to the VM environment, which ensures logical isolation and mobility across the cloud infrastructure.
Which of the following statements is false about the graphical user interface (GUI) and the command-line interface (CLI) of Linux?
Options:
The CLI is more suitable for routine maintenance than the GUI.
The GUI consumes more system resources than the CLI.
It is more efficient to operate the Linux CLI using the keyboard than to operate the GUI using the mouse.
The GUI has higher permissions than the CLI, allowing it to modify the kernel and hide files.
Answer:
DExplanation:
According to the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing training materials, statement D is FALSE. In the Linux operating system, permissions are determined by the User ID (UID) and the specific privileges of the account logged in (such as the root user), not by the type of interface being used. Whether an administrator uses a Graphical User Interface (GUI) or a Command-Line Interface (CLI), the ability to modify the kernel or change system files is strictly governed by the OS's access control lists and kernel-level security modules. In many enterprise cloud environments, such as those running Huawei’s EulerOS, the GUI is often not even installed to reduce the attack surface and save resources.
The other statements are technically correct. Statement A is true because the CLI allows for automation through scripting, making it far superior for routine maintenance and batch processing. Statement B is true because a GUI requires a display server (like X11 or Wayland) and a desktop environment, which significantly increase CPU and memory overhead compared to the text-based CLI. Statement C is true because an experienced administrator can execute complex tasks with a few keystrokes in the CLI much faster than navigating multiple windows and menus in a GUI. In the official curriculum, it is emphasized that for cloud data centers, the CLI is the primary tool for O&M (Operation and Maintenance) because it provides a direct, high-performance link to the system shell. The idea that a GUI provides "higher permissions" is a common misconception; in fact, critical kernel modifications are almost exclusively performed via the CLI or system configuration files to ensure precision and auditability.
====================
In Huawei FusionAccess, Huawei Desktop Protocol (HDP) classifies displayed bitmaps. It uses a lossless compression algorithm for text and a lossy compression algorithm for nonsensitive data, saving bandwidth without compromising user experience.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
Huawei Desktop Protocol (HDP) is a proprietary protocol optimized for cloud desktop scenarios and is a key topic in the FusionAccess learning scope.
HDP usesintelligent bitmap classification:
Text and fine detailsuselossless compressionto ensure clarity and readability.
Images, videos, and nonsensitive graphicsuselossy compression, which significantly reduces bandwidth consumption while maintaining acceptable visual quality.
This adaptive compression strategy allows FusionAccess to deliversmooth user experienceeven in limited bandwidth environments, which is a highlighted advantage in HCIA materials.
Therefore, the statement isTRUE.
FusionCompute adopts hardware-assisted virtualization technology to reduce memory virtualization overhead.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
Huawei FusionCompute leverageshardware-assisted virtualization technologiessuch asIntel VT-x, EPT, and AMD-V, which significantly reduce the overhead associated with CPU and memory virtualization.
Memory virtualization traditionally involved complex software-based address translation, which introduced performance overhead. With hardware-assisted features such asExtended Page Tables (EPT), memory mapping is handled directly by the CPU, improving efficiency and performance.
This approach is explicitly highlighted in HCIA–Cloud Computing materials as a key reason why FusionCompute delivers near-native performance for virtual machines.
Therefore, the statement isTRUE.
To enhance the security of user desktops, FusionAccess supports diverse access management policies. Which of the following statements about access management policies are true?
Options:
MAC address-based access control. This policy can be applied only to users or user groups.
Time-based access control. This policy implements only whitelist control. Users can log in to desktops only in the specified time segment.
IP address-based access control. This policy implements blacklist and whitelist control and allows configuring a single IP address or IP address segment.
Certificate-based access control. This policy is applied globally.
Answer:
A, B, C, DExplanation:
In the official Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing documentation, specifically the "FusionAccess Security" module, the system is described as having a multi-layered security architecture. These four access management policies are the primary tools used to control entry into the virtual desktop environment.
MAC address-based control (A)allows administrators to bind specific users or groups to authorized hardware devices. This ensures that even if a password is compromised, the user can only log in from a company-issued terminal.Time-based control (B)functions as a whitelist; it defines a "valid window" (e.g., 08:00 to 18:00) during which desktop access is permitted. Outside of these hours, the system rejects connection attempts, which is critical for managing contractors or ensuring compliance with labor regulations.
IP address-based control (C)is highly flexible, supporting both blacklists (to block known malicious ranges) and whitelists (to allow only local office subnets). Administrators can define these rules for individual IPs or entire CIDR blocks. Finally,Certificate-based control (D)provides the highest level of identity assurance. Unlike the other policies which can be granular, certificate authentication is typically a global system setting in the ITA/HDC configuration. When enabled, every client must present a valid digital certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) before they are even prompted for a username and password.
By combining these policies, Huawei FusionAccess creates a "Zero Trust" style environment where access is granted based on the user's identity, their physical device, their location (IP), and the time of day. Understanding how to configure these policies in theITA (IT Adapter)portal is a key requirement for the HCIA-Cloud Computing certification and essential for maintaining a secure enterprise desktop cloud.
====================
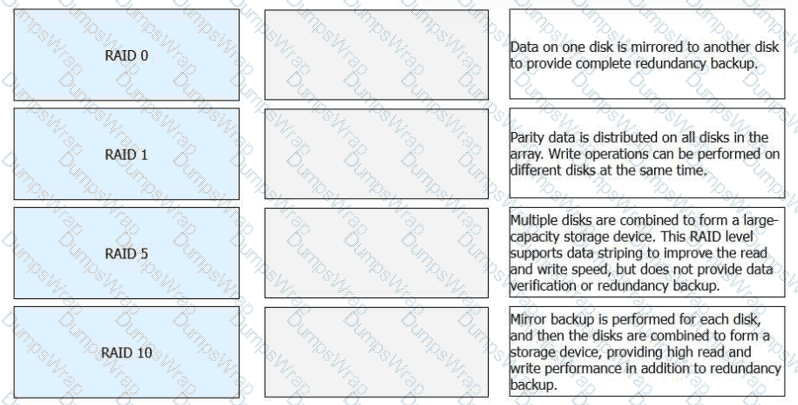
Match the following RAID levels with their respective descriptions.
Options:
Answer:

Explanation:
RAID 0
➡Multiple disks are combined to form a large-capacity storage device. This RAID level supports data striping to improve read and write speed, but does not provide data verification or redundancy backup.
RAID 1
➡Data on one disk is mirrored to another disk to provide complete redundancy backup.
RAID 5
➡Parity data is distributed on all disks in the array. Write operations can be performed on different disks at the same time.
RAID 10
➡Mirror backup is performed for each disk, and then the disks are combined to form a storage device, providing high read and write performance in addition to redundancy backup.
Which of the following statements isfalseabout virtualization concepts?
Options:
A guest OS is the operating system running on a virtual machine (VM).
A guest machine is a virtual machine (VM).
A host machine is a physical machine.
A host OS is the virtualization software layer.
Answer:
DExplanation:
The HCIA–Cloud Computing syllabus clearly defines the basic terminology used in virtualization.
OptionAis correct. Aguest OSrefers to the operating system installed and running inside a virtual machine.
OptionBis correct. Aguest machineis another term for a virtual machine (VM).
OptionCis correct. Ahost machinetypically refers to thephysical serverthat provides hardware resources for virtualization.
OptionDis false. Ahost OS is not the virtualization software layer. The virtualization layer is thehypervisor(such as KVM, Xen, or FusionCompute). In some architectures, the host OS and hypervisor may coexist, but they arenot the same concept.
Therefore, the false statement isD.
FusionCompute integrates physical CPU and memory resources on hosts into a compute resource pool and divides the resources into virtual CPU and memory resources for VMs. The compute resources actually used by a VM cannot exceed the specifications of the hardware resources on the host because the CPU and memory resources used by the VM must be provided by the same host. If this host malfunctions, the system automatically assigns another host to the VM to provide compute resources.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
AExplanation:
This statement is TRUE and covers two fundamental concepts within the Huawei HCIA-Cloud Computing curriculum: resource locality and High Availability (HA).
First, the statement addresses the constraint ofresource locality. In the current architecture of Huawei FusionCompute (and most mainstream virtualization platforms), a single Virtual Machine (VM) cannot "span" its core compute resources (vCPU and RAM) across multiple physical hosts simultaneously. For instance, if a physical host has 128GB of RAM, you cannot create a single VM with 256GB of RAM, because that VM’s memory address space must be mapped to the physical DIMMs of a single physical server to maintain performance and synchronization. Therefore, the maximum specifications of a VM are always bounded by the physical hardware limits of a single host within the cluster.
Second, the statement accurately describes theHigh Availability (HA)function. While a running VM is tied to one host, cloud computing overcomes this physical dependency through cluster-level management. When theVRM (Virtual Resource Management)node detects that a physical host has malfunctioned (via heartbeat loss), it triggers the HA policy. Since the VM’s disk files are stored on shared storage (like a SAN or NAS), the system "assigns" the VM to a different healthy host in the same cluster. The VM is then automatically restarted on that new host, which provides the necessary CPU and memory resources to resume services.
This combination of strict host-level resource allocation for execution and cluster-level flexibility for recovery is what allows Huawei’s cloud solutions to provide stable, enterprise-grade infrastructure. Understanding that compute resources are provided by a "single host" at runtime, but protected by the "cluster" during a failure, is a core objective of the HCIA-Cloud Computing certification.
On FusionAccess, modifying or deleting a full copy template will affect the virtual machines created using the template.
Options:
TRUE
FALSE
Answer:
BExplanation:
In FusionAccess, full copy desktops are created by completely copying the template into an independent virtual machine. After the VM is created, it no longer depends on the template.
According to HCIA–Cloud Computing materials:
Modifying or deleting a full copy template does not affect already provisioned desktops.
Only linked clone desktops depend on the template and snapshot chain.
Therefore, the statement is FALSE.

