Certified - Electronic Fetal Monitoring Questions and Answers
When R-R intervals are short, the fetal heart rate is
Options:
fast
normal
slow
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract NCC-Recommended Sources
The fetal heart rate is calculated from the interval between consecutive R waves in the fetal ECG. Shorter R-R intervals indicate more beats per unit of time, therefore resulting in a higher heart rate. AWHONN and Menihan both note that fetal ECG monitoring measures instantaneous rate based on R-R spacing, and “shorter intervals correspond to fetal tachycardia.”
Simpson & Creehan reinforce that fetal heart rate variability and baseline are derived from these R-R intervals, with shorter intervals consistently producing faster rates. Miller’s Pocket Guide describes the relationship simply: “Short R-R = faster rate; long R-R = slower rate.”
Maternal fever can cause fetal tachycardia because the increased maternal temperature:
Options:
Decreases tissue perfusion
Increases fetal metabolism
Inhibits catecholamine release
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Maternal hyperthermia—most commonly from infection—causes a rise in fetal temperature, which increases fetal metabolic rate. The fetus responds by increasing heart rate to meet the increased oxygen demand.
Effects include:
Increased fetal oxygen consumption
Enhanced fetal cardiac output
Resultant tachycardia, often 160–180 bpm
This mechanism is repeatedly outlined in NCC’s physiology domain, AWHONN, Menihan, Simpson, and Creasy & Resnik.
Option A is incorrect because maternal fever does not reduce perfusion.
Option C is incorrect because catecholamines are often elevated, not inhibited.
Thus, the mechanism is increased fetal metabolism.
When documenting the occurrence of late decelerations in the medical record, what should be charted?
Options:
Components of the tracing
Notation that the tracing was normal or abnormal
Tracing category
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
According to NCC, AWHONN, and evidence-based documentation standards, clinicians must document:
Baseline
Variability
Accelerations
Decelerations (type, depth, duration, timing)
Uterine activity
This fulfills the NICHD 3-tier system and legal documentation expectations.
Why the incorrect answers are wrong:
B. "Normal/abnormal" → vague, not an acceptable documentation standard.
C. Category alone → insufficient; categories must be supported by the components.
Amnioinfusion can cause what changes in the fetal heart rate tracing?
Options:
Improvement in fetal heart rate variability
Increase in fetal heart rate baseline
Resolution of variable decelerations
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
NCC defines amnioinfusion as indicated for:
Recurrent variable decelerations caused by cord compression
Oligohydramnios reducing buffer around the cord
Expected effect:
Reduction or elimination of variable decelerations
Why the other answers are incorrect:
A. Variability does not improve with amnioinfusion.
B. Baseline FHR does not increase as a result of amnioinfusion.
Correct answer: C. Resolution of variable decelerations.
Intermittent fetal heart rate auscultation for a low-risk, spontaneous laboring patient who is 4–5 centimeters dilated should be assessed at intervals every
Options:
5–10 minutes
15–30 minutes
45–60 minutes
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract (No URLs or Links)
NCC aligns with AWHONN’s “Practice Guidelines for Fetal Heart Monitoring”, which specify the appropriate frequency of intermittent auscultation (IA) based on labor phase and risk level. For low-risk patients in active labor, IA must occur:
Every 15–30 minutes during active labor
Every 5 minutes during second stage with pushing
AWHONN and Menihan emphasize that intermittent auscultation must follow standardized time intervals to ensure adequate fetal surveillance. These intervals reflect the physiologic understanding that fetal compromise may evolve over relatively short time periods, and active labor (4–7 cm dilation) represents a time of increasing stress on fetal oxygenation.
Simpson & Creehan explain that IA frequency should increase as labor intensifies, and that the 15–30-minute interval is the nationally recognized standard for low-risk active labor. NCC’s exam content domain “Fetal Assessment Methods” reinforces knowing these surveillance intervals for safe low-intervention care.
Thus, for a 4–5 cm dilated, low-risk, spontaneous labor, the correct IA interval is every 15–30 minutes.
References (No URLs)
NCC C-EFM Candidate Guide 2025 – Fetal Assessment Methods
AWHONN Practice Guidelines for Fetal Heart Monitoring, 2022–2024
Menihan: Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Simpson & Creehan: Perinatal Nursing
Miller: Fetal Monitoring Pocket Guide
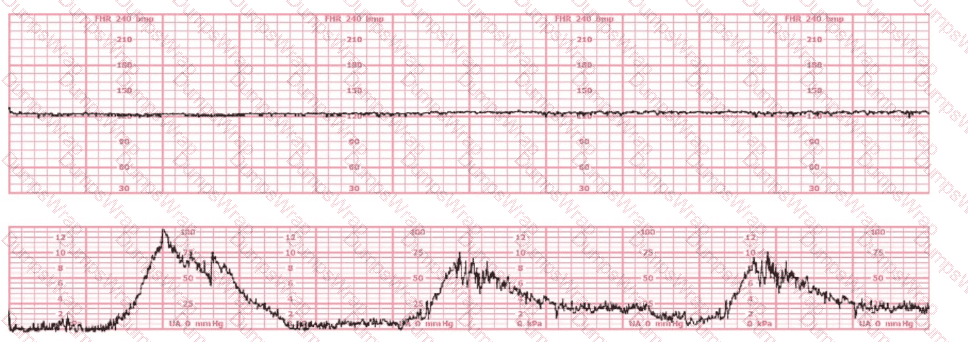
The tracing shown is from a woman at 28-weeks gestation in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) after an appendectomy. She is alert and awake. Based on this fetal heart rate pattern, the most appropriate intervention is:
Options:
Administer terbutaline
Continued monitoring
Perform cesarean birth
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
The fetal heart rate tracing shows:
Baseline around 140 bpm
Minimal variability
No accelerations
No decelerations
Regular uterine activity but not tachysystole
This pattern is Category II, but in the context of:
28-week gestation
Immediate postoperative status after anesthesia
Maternal alertness and stability
NCC and AWHONN emphasize that maternal sedation, post-anesthesia effects, medications, and physiologic stress commonly cause temporary minimal variability without acidemia, especially at preterm gestations where baseline variability is normally lower.
Key NCC principle:
Minimal variability in a stable mother without decelerations does NOT require emergent delivery.
Instead, the fetus should be observed as anesthesia effects wear off.
Why other answers are incorrect:
A. Terbutaline – No tachysystole and no recurrent decels are present.
C. Cesarean birth – No bradycardia, no late decels, no absent variability, and no Category III criteria.
Thus, appropriate management is B. Continued monitoring.
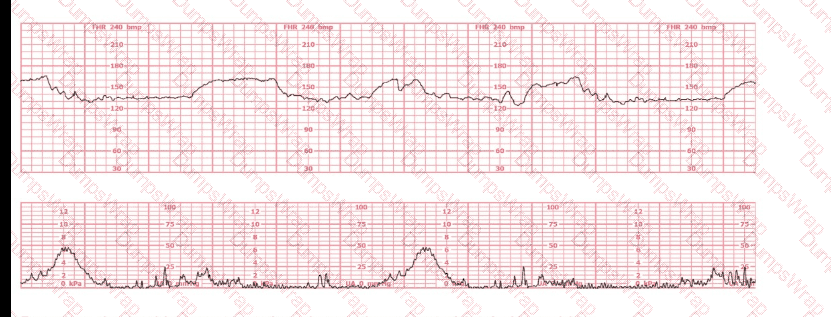
Based on the fetal heart rate tracing shown, the expected fetal pH would be:
Options:
Above 7.15
Below 7.15
Unaffected by the fetal heart rate
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Assessment of likely fetal acid–base status is grounded in NCC-aligned principles that correlate fetal pH with fetal heart rate patterns, especially variability, presence/absence of accelerations, and type and depth of decelerations.
This tracing shows the following features:
Baseline:
The fetal heart rate baseline is approximately 140–150 bpm, within the normal 110–160 bpm range.
Variability:
Moderate variability is present—approximately 6–25 bpm amplitude.
Per NCC and NICHD definitions, moderate variability is strongly associated with normal fetal oxygenation and normal fetal pH > 7.20–7.25.
Accelerations:
There are occasional small accelerations, another strong indicator of normal fetal acid–base status.
Decelerations:
The tracing shows occasional variable decelerations, shallow and brief, recovering rapidly, typical of intermittent cord compression.
NCC references emphasize that intermittent, non-recurrent variables with moderate variability do not correlate with acidemia.
Uterine activity:
Contractions are present but not excessive, and fetal response remains reassuring.
Correlating tracing features with fetal pH (per NCC, AWHONN, Simpson, Menihan):
Moderate variability is the strongest intrapartum indicator of normal fetal pH.
The NICHD/NCC consensus repeatedly states that:
“The presence of moderate variability reliably predicts adequate fetal oxygenation and a fetal pH above the threshold associated with metabolic acidemia.”
Fetal pH below 7.15 is associated with:
Absent variability
Recurrent late decelerations
Recurrent deep variable decelerations
Prolonged bradycardia
None are present in this tracing.
Because the tracing demonstrates moderate variability, intermittent uncomplicated variables, and no recurrent late decelerations, the physiologic expectation is that the fetal pH remains normal, significantly above 7.15.
Therefore, the correct answer is: A (above 7.15).
A woman at 34-weeks gestation is in active labor after spontaneous rupture of membranes. Accelerations should be documented as

Options:
absent
present 10×10
present 15×15
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract (No URLs)
For fetuses before 32–34 weeks, the National Certification Corporation (NCC) follows the physiologic standards established by AWHONN, Simpson & Creehan, Menihan, and Creasy & Resnik, which emphasize that preterm fetuses have less mature autonomic nervous system development, resulting in smaller and shorter accelerations.
According to the NCC C-EFM Exam Content Outline (Pattern Recognition & Intervention) and the AWHONN Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles (2022–2024):
Preterm fetuses (<32 weeks) normally demonstrate 10 bpm × 10 sec accelerations.
By approximately 32–34 weeks, accelerations may begin transitioning toward 15×15, but the accepted standard for documentation at 34 weeks remains 10×10, unless clearly meeting 15×15 criteria.
NCC emphasizes using gestational-age–appropriate criteria for documenting accelerations, because autonomic reactivity increases gradually and is not fully comparable to term until after 32–34 weeks.
Menihan’s Electronic Fetal Monitoring also states that preterm fetuses “should be evaluated with the 10×10 rule until it is clear that the fetus is demonstrating mature 15×15 acceleratory capacity.”
Simpson & Creehan reinforce this point, noting that accelerations in late preterm gestations “may not consistently reach 15 bpm for 15 seconds, and thus 10×10 remains the appropriate designation.”
Since the patient is 34 weeks, the fetus is late-preterm and may not reliably meet the full 15×15 criteria; therefore, the correct documentation standard remains 10×10.
Thus, accelerations should be charted as:
“Present 10×10.”
References
NCC C-EFM Candidate Guide 2025 – Content Domain: Pattern Recognition and Intervention
AWHONN Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles & Practices, 2022–2024
Menihan: Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Concepts and Applications
Simpson & Creehan: Perinatal Nursing
Miller: Fetal Monitoring Pocket Guide
Creasy & Resnik: Maternal–Fetal Medicine
A reliable indicator of fetal oxygenation is fetal
Options:
heart rate accelerations
movement
regular sleep–wake cycles
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract NCC-Recommended Sources
AWHONN and NICHD definitions state that fetal accelerations are a strong indicator of adequate fetal oxygenation and neurologic integrity. Accelerations reflect intact sympathetic and parasympathetic balance and adequate oxygen reserve.
Simpson & Creehan emphasize accelerations as “the most reliable sign of fetal well-being,” because they require intact autonomic function, sufficient pH, and adequate oxygenation. Menihan also identifies accelerations as the most reassuring feature on a fetal heart tracing.
Fetal movement is helpful but not directly reflective of oxygenation, as movements can decline for non-hypoxic reasons (sleep cycles, maternal sedation). Regular sleep–wake cycles are normal developmental neurologic patterns and not oxygenation markers.
Creasy & Resnik reinforce that “presence of accelerations reliably indicates absence of metabolic acidemia.”
Fetal heart rate variability results from normal variance in fetal:
Options:
Cardiac responsiveness
Levels of carbon dioxide
R–R intervals
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Variability reflects the interplay of the autonomic nervous system—sympathetic and parasympathetic influences—on the fetal myocardium. NCC defines variability as variation in the R–R intervals on the fetal ECG.
Key points:
Variability originates from beat-to-beat fluctuations in ventricular depolarization timing.
These R–R interval changes result from baroreceptor and chemoreceptor responses, vagal modulation, and fetal behavioral states.
Carbon dioxide levels affect chemoreceptors but do not directly define variability.
Thus, variability is best described as resulting from variance in R–R intervals.
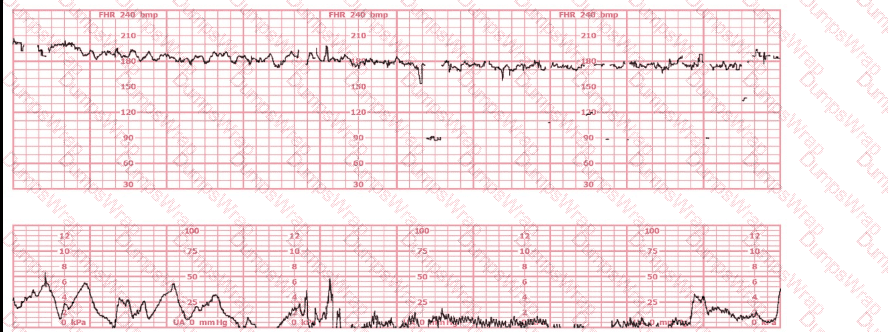
A 30-year-old woman (G2P0) is experiencing preterm labor at 26-weeks gestation. She is receiving magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection. Her external fetal monitoring tracing over the past 30 minutes is shown. The next step would be to:
Options:
Administer acetaminophen
Discontinue magnesium sulfate
Evaluate for chorioamnionitis
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
This tracing shows:
Baseline ~170–175 bpm → fetal tachycardia
Minimal variability
No contractions of significance
Maternal treatment with magnesium sulfate, which typically decreases baseline and variability—not increase it
NCC and AWHONN physiology guidelines emphasize that fetal tachycardia is most commonly associated with maternal infection, including chorioamnionitis, especially in preterm labor.
Magnesium sulfate does not cause tachycardia; it generally causes:
↓ baseline
↓ variability
Thus, fetal tachycardia + minimal variability in a preterm patient strongly suggests maternal infection, requiring evaluation for chorioamnionitis.
Why the wrong answers are incorrect:
A. Acetaminophen → used after confirming fever, not before evaluating the cause.
B. Discontinuing magnesium → magnesium sulfate does not cause tachycardia; discontinuing it removes fetal neuroprotection.
The success of interventions to treat fetal hypoxia first depends on:
Options:
Improving maternal oxygenation
Minimizing uterine activity
Optimizing uteroplacental blood flow
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
NCC/AWHONN emphasize that the primary goal of intrauterine resuscitation is to:
Optimize uteroplacental blood flow, which restores fetal oxygen delivery.
Key measures include:
Maternal repositioning (lateral)
Reducing tachysystole
IV fluid bolus
Correcting maternal hypotension
Stopping oxytocin
Treating underlying causes
Improving maternal oxygenation is supportive, but improving uteroplacental perfusion is the critical first determinant of resuscitation success.
Why the other answers are not first priority:
A. Oxygen — optional and no longer universally recommended unless maternal hypoxemia exists.
B. Minimizing uterine activity — essential, but still secondary to restoring perfusion.
Correct answer: C. Optimizing uteroplacental blood flow
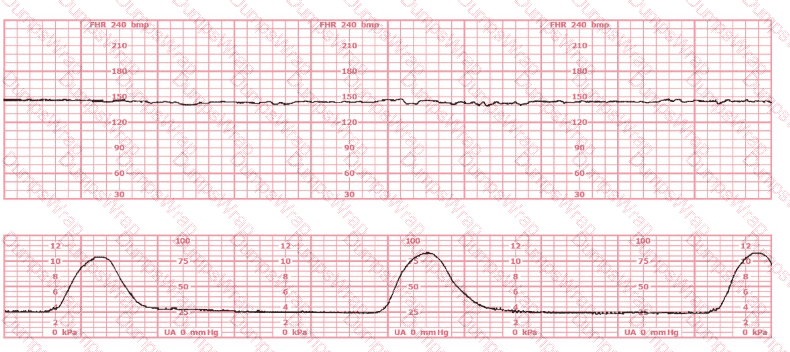
The most probable underlying fetal physiologic cause for this tracing would be:
Options:
Myocardial hypoxic depression
Release of catecholamines
Vagal nerve stimulation in response to hypoxemia
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
This tracing shows:
Baseline ~145 bpm
Minimal variability
No accelerations or decelerations
Very little fluctuation → resembles a flat/minimal variability Category II tracing
The key physiologic mechanism behind minimal variability in the presence of a normal baseline and normal contraction pattern is most often:
Increased fetal sympathetic tone, driven by catecholamine release (epinephrine and norepinephrine).
NCC and AWHONN explain:
Catecholamine release (due to fetal stress, early hypoxemia, or maternal stress) results in:
Reduced beat-to-beat fluctuation
Minimal baseline variability
This is considered an early compensatory mechanism, not yet a decompensated hypoxic state.
Why the other answers are incorrect:
A. Myocardial hypoxic depression
Causes absent variability, NOT minimal variability.
Represents advanced or severe hypoxia. The FHR here is not absent variability.
C. Vagal stimulation in response to hypoxemia
Produces decelerations, especially late or prolonged.
This strip shows no decelerations, ruling this out.
Therefore the most accurate physiologic explanation is B. Release of catecholamines.
The decelerations seen in the fetal monitoring tracing shown are best described as:
Options:
Early
Late
Variable
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Accurate classification of decelerations requires evaluating their shape, onset, nadir, recovery, relationship to contractions, and variability characteristics. NCC uses the NICHD standardized definitions, reinforced across AWHONN, Miller’s Pocket Guide, Menihan, Simpson, and Creasy & Resnik.
Key features in this tracing:
Abrupt onsetThe FHR drops rapidly from baseline to nadir in less than 30 seconds—this is the defining hallmark of a variable deceleration per NICHD.
Sharp V-shape and deep amplitudeThe tracing shows steep descents and ascents, characteristic of cord compression–type variable decelerations.
Inconsistent timing with contractionsThe decelerations do not begin at the start of contractions (as early decelerations would) and do not consistently begin after the peak of contractions (as late decelerations would). Variable decelerations can occur before, during, or after a contraction—exactly what is demonstrated here.
Rapid return to baselineAnother core feature of variable decelerations in NICHD/NCC definitions.
No uniform contraction relationshipEarly decelerations are symmetrical and mirror contractions. Late decelerations begin after the peak of the contraction. This strip does not match either pattern.
Differentiation per NCC-aligned definitions:
Early Decelerations:Gradual onset (>30 sec), nadir mirrors contraction peak, shallow, uniform.Not present.
Late Decelerations:Gradual descent, nadir after contraction peak, smooth shape.Not present.
Variable Decelerations:Abrupt onset (<30 sec), variable timing, sharp V-shape, rapid recovery, often with shoulders.Exactly matches the tracing.
Therefore, according to NICHD/NCC criteria, the decelerations shown are variable decelerations.
The pattern on the fetal heart rate tracing shown is likely due to

Options:
fetal head compression
placental insufficiency
umbilical cord compression
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract Sources:
The tracing demonstrates an abrupt-onset, sharp, V-shaped deceleration, occurring simultaneously with or slightly after a contraction—classic for variable decelerations, which are caused by umbilical cord compression.
According to AWHONN Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles & Practices, variable decelerations are defined by:
“Abrupt decreases in FHR below baseline of at least 15 bpm, lasting at least 15 seconds and less than 2 minutes.”
“Most commonly associated with umbilical cord compression, whether transient or recurrent.”
Physiology reference (Simpson & Miller, Pocket Guide):
Compression of the umbilical vein causes a brief acceleration.
Compression of the umbilical arteries triggers a vagal response, producing a rapid deceleration.
This creates the characteristic sharp ‘V’, ‘U’, or ‘W’ shape on the monitor.
Placental insufficiency (Choice B) produces late decelerations, which are gradual, not abrupt.
Fetal head compression (Choice A) produces early decelerations, which mirror contractions and have a gradual pattern.
Thus, the tracing is most consistent with variable decelerations caused by umbilical cord compression.
An electronic fetal monitoring factor that best correlates with fetal well-being is:
Options:
Absence of decelerations
Baseline heart rate 140–150 bpm
Presence of variability
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
The single best indicator of fetal oxygenation and neurologic integrity is:
Moderate baseline variability
Variability reflects:
Normal autonomic regulation
Adequate fetal oxygenation
Intact neurologic pathways
Absence of decelerations is helpful but not as predictive.
Baseline FHR (e.g., 140–150) is normal, but baseline alone does not confirm well-being.
Correct answer: C. Presence of variability
This fetal heart rate tracing is of a woman in labor with dichorionic-diamniotic twins at 36-weeks gestation, 4 cm dilated. She is on oxygen via face mask. Based on the fetal heart rate tracing, what is the most appropriate action?
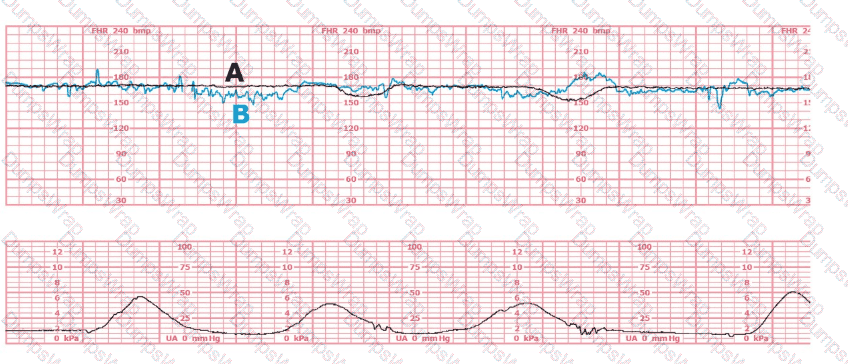
(Tracing A = black; Tracing B = blue)
Options:
Cesarean birth
Continue to observe
Give terbutaline
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
Both fetal tracings (A and B) show:
Baselines around 140–150 bpm
Moderate variability
Intermittent accelerations
No recurrent decelerations
Normal contraction pattern
Overall Category I patterns for both twins
NCC, NICHD, and AWHONN emphasize that moderate variability with a normal baseline is the strongest reassurance of fetal well-being, even in multifetal gestations.
There is no evidence of:
Tachysystole
Recurrent variables
Recurrent lates
Prolonged decelerations
Category III patterns
Therefore, the appropriate action is ongoing observation.
Why the incorrect answers are wrong:
A. Cesarean birth — Not indicated with Category I FHR patterns.
C. Terbutaline — Reserved for tachysystole or prolonged deceleration patterns, not present here.
This tracing reflects
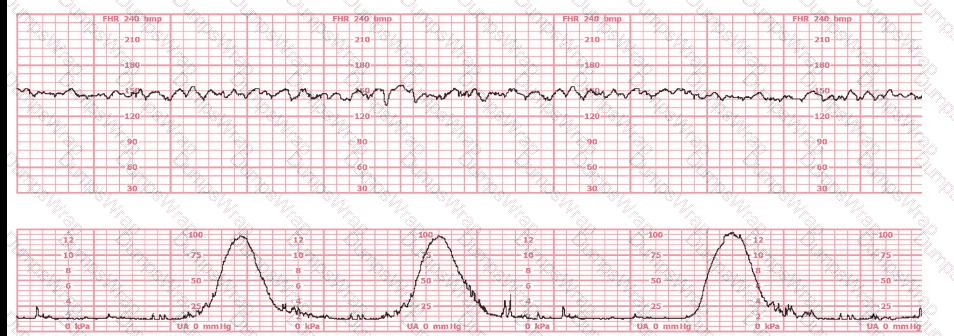
Options:
Minimal variability
Moderate variability
Sinusoidal pattern
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract (NCC-Recommended Sources Only)
The fetal heart rate (FHR) tracing shown demonstrates a baseline approximately 135–145 bpm with fluctuations of 6–25 bpm, a hallmark of moderate variability. Moderate variability is defined in all NCC-endorsed resources as the normal amplitude range of 6–25 bpm around the fetal baseline.
According to the AWHONN Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles & Practices (2022–2024), moderate variability is considered the single most reliable indicator of adequate fetal oxygenation and intact neurologic pathways, specifically reflecting well-functioning sympathetic and parasympathetic interplay.
The NICHD/NCC standardized definitions included in the NCC C-EFM Candidate Guide state:
Minimal variability: amplitude range ≤ 5 bpm
Moderate variability: amplitude range 6–25 bpm
Marked variability: amplitude > 25 bpm
Sinusoidal pattern: smooth, undulating waveform, 3–5 cycles per minute, equal amplitude, absent beat-to-beat variability
The tracing provided does not show the repetitive, smooth, wave-like pattern of a sinusoidal rhythm; nor does it show flattening associated with minimal variability. Instead, it includes continuous beat-to-beat fluctuation within the moderate range, without periods of absent or minimal variability.
Menihan’s Electronic Fetal Monitoring (5th ed.) and Simpson & Creehan’s Perinatal Nursing (5th ed.) both emphasize that moderate variability is:
A reassuring feature
Indicative of adequate fetal CNS oxygenation
Expected in a reactive, well-oxygenated fetus
A key criterion for Category I classification
Additionally, Miller’s EFM Pocket Guide reiterates that variability between 6–25 bpm is considered the normal (moderate) fetal autonomic response and is not a sinusoidal pattern, which has a fixed amplitude and frequency.
Therefore, based on NCC-standard definitions and the observed amplitude, the correct interpretation is moderate variability.
References (No URLs):
AWHONN Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles & Practices; NCC C-EFM Candidate Guide 2025; Simpson & Creehan Perinatal Nursing; Menihan Electronic Fetal Monitoring; Miller’s Pocket Guide to Fetal Monitoring; Creasy & Resnik Maternal-Fetal Medicine.
Maternal–fetal exchange during labor is diminished by:
Options:
An increase in maternal cardiac output
Open-glottis pushing in second stage
Placental calcifications
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
Placental calcifications:
Reduce surface area for maternal–fetal gas exchange
Impair placental perfusion
Are associated with post-dates and chronic insufficiency
Decrease the placenta’s ability to oxygenate the fetus
Why the incorrect answers are wrong:
A. Increased maternal cardiac output → improves uteroplacental perfusion.
B. Open-glottis pushing → improves oxygenation compared with closed-glottis Valsalva pushing.
Correct answer: Placental calcifications.
When monitoring monochorionic-monoamniotic twins, which of the following fetal heart rate patterns would be anticipated?
Options:
Baseline tachycardia
Minimal variability
Variable decelerations
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract (NCC-Referenced Sources)
Mono-mono twins share a single amniotic cavity, which significantly increases the risk of cord entanglement, a concept highlighted in AWHONN FHM, Creasy & Resnik Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and Miller’s EFM Pocket Guide.
These texts emphasize:
“Cord entanglement is nearly universal in monoamniotic twins.”
“Variable decelerations are common due to recurrent cord compression.”
Baseline tachycardia or minimal variability are not expected baseline characteristics, but may appear only in pathologic circumstances.
Thus, variable decelerations are the expected and anticipated FHR pattern in mono-mono twins.
A patient presents at 38-weeks gestation with complaints of decreased fetal movement and ruptured membranes. The fetal heart rate is not able to be determined with an external ultrasound monitor. A spiral electrode is placed, and the tracing shows a rate of 90 bpm. What is the next most appropriate action?
Options:
Intrauterine resuscitation measures
Palpation of the maternal radial pulse
Request for an urgent bedside ultrasound
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Whenever a fetal heart rate is unexpectedly low (such as 90 bpm), the FIRST step per NCC and AWHONN is to confirm that the signal is fetal, not maternal.
Even internal spiral electrodes can capture maternal heart rate, especially after:
Rupture of membranes
Maternal hypotension
Maternal dehydration
Maternal tachycardia or bradycardia
Thus, the first, most immediate action is:
→ Palpate the maternal radial pulse to determine whether the tracing is maternal or fetal.
If rates match → the monitor is falsely detecting the maternal pulse.
If rates differ → confirm true fetal bradycardia and begin intrauterine resuscitation.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Intrauterine resuscitation — should NOT begin before confirming the tracing is fetal.
C. Bedside ultrasound — appropriate after confirming that the tracing is not maternal, not before.
Correct answer: B. Palpation of the maternal radial pulse.
A patient at 41 weeks gestation is being induced. She has progressed slowly and is now at 6 cm, 90% effaced, –1 station. She has the fetal heart tracing shown despite repositioning. The next step in the management of this patient should be to:

Options:
Apply a spiral electrode
Decrease the oxytocin
Perform an amnioinfusion
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
The tracing clearly shows recurrent deep variable decelerations, characterized by:
Abrupt onset (<30 sec)
Sharp V-shape
Rapid descent and ascent
Depth exceeding 60–70 bpm drops
Occurring with most contractions
This pattern is highly consistent with cord compression, which is the physiologic basis of variable decelerations. According to NCC, NICHD, AWHONN, Miller, and Menihan, recurrent (≥50% of contractions) deep variables with slow return to baseline indicate fetal compromise and require targeted intervention.
The patient has already been repositioned, so first-line management has failed. NCC emphasizes that the next recommended intervention for recurrent variable decelerations, particularly when maternal repositioning is ineffective, is amnioinfusion. This intervention relieves cord compression by restoring fluid around the umbilical cord.
Why the other choices are incorrect:
A. Apply a spiral electrode – NOT appropriate
Spiral electrodes improve signal quality but do not treat cord compression.
The tracing is already clearly interpretable, and the issue is physiologic, not technical.
B. Decrease the oxytocin – Not the best next step
Decreasing oxytocin is appropriate when tachysystole is contributing to fetal intolerance.
This strip shows normal contraction frequency (about every 2–3 minutes) and no tachysystole.
Thus, reducing oxytocin alone will not relieve cord compression.
C. Perform an amnioinfusion – CORRECT
NCC-approved references repeatedly state:
For recurrent variable decelerations that persist after maternal repositioning, amnioinfusion is recommended to reduce the frequency and depth of decelerations.
It can improve fetal oxygenation, decrease cord compression, and reduce the need for operative delivery.
It is the intervention most directly targeted to the pathophysiology of this pattern.
Therefore, C. Perform an amnioinfusion is the correct next management step.
This tracing demonstrates:
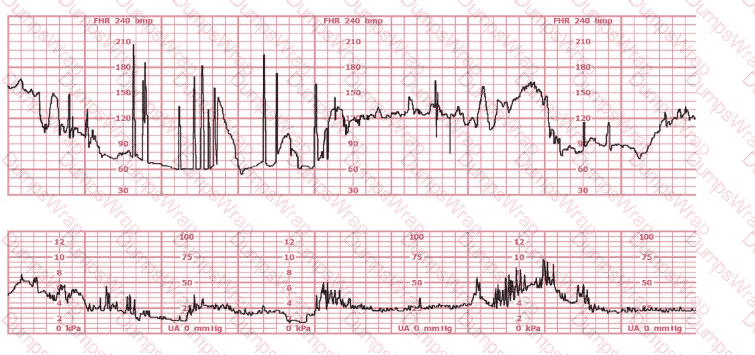
Options:
Bradycardia
Category III tracing
Prolonged deceleration
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
A prolonged deceleration is defined by NICHD and NCC as:
A deceleration lasting ≥2 minutes but <10 minutes
Decrease in FHR of ≥15 bpm
Can occur with or without uterine contractions
This tracing shows:
A deep drop in FHR down to ~60–70 bpm
Duration lasting several minutes
Recovery back to baseline
Moderate variability present afterward
Because variability remains present and the tracing does not show:
Absent variability
Recurrent late decelerations
Recurrent variable decelerations with absent variability
Bradycardia for ≥10 minutes
…it does not meet criteria for Category III.
It is also not bradycardia, because bradycardia requires:
Baseline <110 bpm for 10 minutes or longer
Therefore the correct interpretation is a prolonged deceleration.
The main reason intrauterine pressure catheters are placed is to:
Options:
Define the quality of the fetal baseline
Determine the contraction pattern
Rule out artifact
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Intrauterine pressure catheters (IUPCs) are an internal uterine activity monitoring device used when external tocodynamometry does not provide adequate assessment of contraction strength or frequency. According to NCC, AWHONN, Miller, and Menihan, the primary indication for placing an IUPC is to obtain accurate, quantitative measurement of uterine activity.
Purpose of IUPC (per NCC and AWHONN):
Measures exact intrauterine pressure in mmHg
Calculates Montevideo units (MVUs) to evaluate adequacy of labor
Clearly differentiates:
Frequency
Duration
Strength (intensity)
Resting tone
NCC explicitly lists the primary purpose as:
“Accurate assessment of uterine contraction pattern and intensity.”
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Define the quality of the fetal baseline – Incorrect
Fetal heart rate (FHR) baseline quality is determined by fetal ECG or FSE, not IUPC.
IUPCs monitor the uterus, not the fetal cardiac signal.
C. Rule out artifact – Incorrect
While an IUPC can reduce artifact from the toco, this is not its primary purpose.
Artifact is more commonly an issue with external FHR monitoring, corrected by repositioning or placing a fetal scalp electrode—not by using an IUPC.
Correct Answer:
B. Determine the contraction pattern
This aligns directly with NCC’s Electronic Monitoring Equipment domain: IUPCs provide the most accurate and reliable measurement of uterine activity when external monitoring is inadequate.
The ratio of oxyhemoglobin to the total amount of hemoglobin available is called oxygen
Options:
affinity
carrying capacity
saturation
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract NCC-Recommended Sources
Oxygen saturation refers to the percentage of hemoglobin binding sites occupied by oxygen. NCC physiology resources, including Simpson & Creehan and Creasy & Resnik, define oxygen saturation as the “ratio of oxyhemoglobin to total hemoglobin”—the same definition used in fetal oxygenation discussions.
Oxygen affinity refers to hemoglobin’s tendency to bind oxygen (related to the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve).
Oxygen carrying capacity refers to the total amount of oxygen hemoglobin can transport, independent of current saturation.
AWHONN and Menihan emphasize that fetal oxygenation assessment is dependent on understanding oxygen saturation, not affinity or carrying capacity, when discussing fetal hypoxemia and gas exchange.
In the event of recurrent variable decelerations with thick meconium, amnioinfusion is recommended to:
Options:
Dilute thick meconium
Restore uterine blood flow
Treat oligohydramnios
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
Amnioinfusion is considered an intrauterine resuscitative intervention used specifically for recurrent variable decelerations caused by cord compression. NCC, AWHONN, Miller, and Menihan consistently teach that variables occur when the umbilical cord becomes compressed, reducing fetal oxygenation. When oligohydramnios or decreased amniotic fluid volume is present, the cord is more vulnerable to compression.
Why amnioinfusion is used:
Amnioinfusion works by:
Increasing intraamniotic fluid volume
Reducing umbilical cord compression
Decreasing the frequency and severity of variable decelerations
This directly targets the pathophysiology behind recurrent variables.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A. Dilute thick meconium – NOT supported by NCC
Historically, amnioinfusion was studied for meconium dilution, but major organizations—including NCC-aligned sources—state that amnioinfusion is NOT recommended for the sole purpose of diluting meconium. It does not reduce meconium aspiration syndrome and is no longer indicated for that purpose.
B. Restore uterine blood flow – NOT accurate
Uterine blood flow is addressed through maternal positioning, fluid bolus, reducing uterine tachysystole, and minimizing vasoconstriction—not via amnioinfusion. Amnioinfusion does not physiologically affect uterine perfusion.
C. Treat oligohydramnios – CORRECT
Recurrent variables with thick meconium often occur in the setting of low fluid, which worsens cord compression.
NCC-recommended indications include:
Recurrent variable decelerations unresponsive to repositioning
Suspected or confirmed oligohydramnios
Thick meconium may be associated with low fluid, but the purpose of amnioinfusion is to alleviate cord compression by restoring fluid volume, not to dilute the meconium.
Thus, the correct answer is C. Treat oligohydramnios.
The fetal heart rate tracing shown demonstrates:
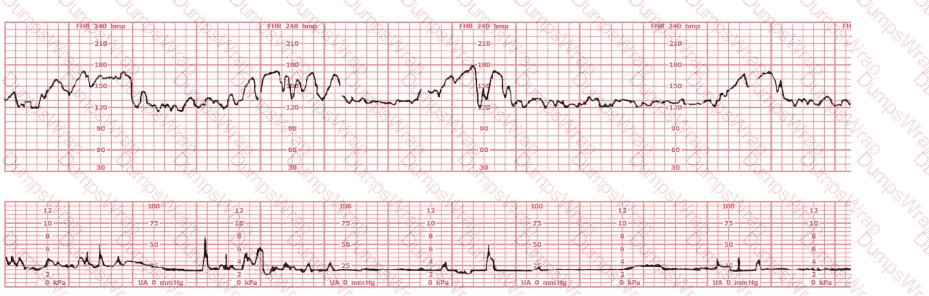
Options:
Accelerations
Category II tracing
Marked variability
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
NCC C-EFM uses NICHD terminology to describe key FHR characteristics: baseline, variability, accelerations, and decelerations. In this strip, the following findings are present:
Baseline:The baseline appears approximately 135–145 bpm, which is within the normal 110–160 bpm range described in NCC and AWHONN materials.
Variability:Beat-to-beat fluctuation is within 6–25 bpm, which meets the definition of moderate variability. NCC and NICHD define moderate variability as amplitude range of 6–25 bpm; this is associated with adequate fetal oxygenation and a normal fetal acid–base status.
Accelerations:The tracing shows distinct increases in FHR above the baseline by at least 15 bpm lasting 15 seconds or more but less than 2 minutes. NCC and NICHD define an acceleration in a term fetus precisely as “a visually apparent abrupt increase in FHR, with peak ≥15 bpm above baseline, lasting ≥15 seconds and <2 minutes.” The pattern shown fits this definition clearly.
Category determination:A tracing with normal baseline, moderate variability, and accelerations without decelerations is classified as Category I, not Category II. Category II is reserved for tracings that are not clearly Category I or III, such as minimal or marked variability, recurrent variables, or prolonged decelerations.
Marked variability consideration:Marked variability is defined as amplitude >25 bpm. While the tracing is somewhat jagged, the fluctuation does not sustain >25 bpm amplitude over a 10-minute segment and instead remains in the moderate range, so it does not meet criteria for marked variability.
Given these observations, the most accurate description of the tracing from the options provided is that it demonstrates accelerations.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve in a healthy fetus will cause:
Options:
Decreased fetal heart rate
Increased cardiac contractility
Increased fetal blood pressure
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
Vagal stimulation is part of the parasympathetic nervous system, which causes:
Slowing of the fetal heart rate (FHR)
Rapid but temporary changes in HR
Seen with head compression, scalp stimulation, or fetal movement
NICHD/NCC physiology explains:
Vagus nerve activation → acetylcholine release → slowed SA node firing → decrease in FHR
This mechanism is responsible for early decelerations during labor due to head compression.
Why the incorrect answers are wrong:
B. Increased cardiac contractility → sympathetic effect, not vagal.
C. Increased fetal blood pressure → also a sympathetic effect.
Correct answer: A. Decreased fetal heart rate
During amnioinfusion, the infusion should be stopped periodically to assess changes in:
Options:
Baseline uterine pressure
Contraction pattern
Patient pain level
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
During amnioinfusion, NCC emphasizes monitoring for uterine overdistention, which can lead to uterine hypertonus, uterine rupture, or placental separation. The primary way to evaluate overdistention is by measuring baseline uterine pressure via IUPC.
Rising resting tone (>20–25 mmHg) indicates accumulating fluid and risk.
Stopping the infusion intermittently allows recalibration and assessment of uterine baseline pressure.
Contraction pattern (option B) is important but not the primary safety parameter.
Pain (option C) is nonspecific and not a reliable indicator of uterine overdistention.
Thus, the infusion is stopped to assess baseline uterine pressure.
A nulliparous woman at term presents with leaking fluid. Rupture of membranes confirmed. After 6 hours she is completely dilated, +2 station, has been pushing 2 hours with oxytocin at 10 mU/min. The fetal tracing is shown. What is the next step in management?
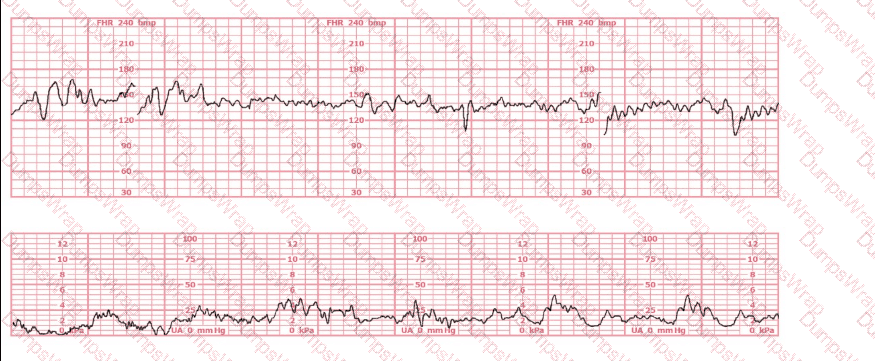
Options:
Continue pushing for another hour
Decrease oxytocin
Expedite birth
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract Without Any URLs or Links:
According to the NCC C-EFM 2025 Exam Content Outline and recommended references such as AWHONN Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles, Simpson & Miller (Fetal Monitoring Text), and Menihan’s EFM Guide, recurrent variable or late decelerations with minimal or moderate variability during the second stage of labor—particularly when the patient has been pushing for ≥2 hours—indicate progressive fetal intolerance of labor.
AWHONN states that when the fetal tracing displays recurrent variable decelerations with ongoing stress from long second stage, the recommended intervention is operative or expedited vaginal birth, provided the fetal station is at +2 or lower. AWHONN and Simpson emphasize that reducing oxytocin is insufficient when the tracing demonstrates ongoing significant decelerations during active pushing with adequate descent.
The NCC blueprint within Pattern Recognition & Intervention emphasizes:
Identifying worsening recurrent decelerations
Acting when fetal tolerance is decreasing
Prioritizing timely intervention when the second stage exceeds standard limits with a non-reassuring tracing
Because she is fully dilated, vertex at +2, and tracing shows recurrent decelerations during pushing, the evidence-based next step is expediting birth, typically via operative vaginal delivery.
(Full question statement)
This tracing is consistent with:
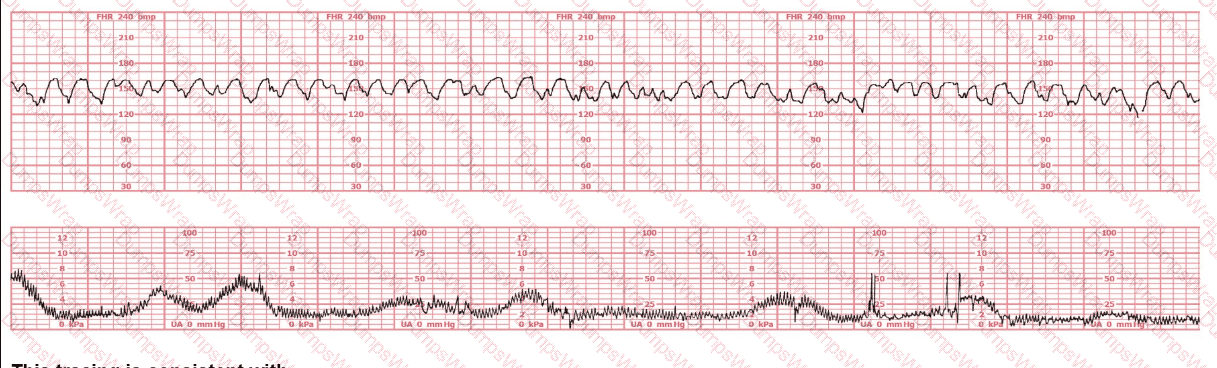
Options:
Atrial flutter
Effects of butorphanol administration
Fetal-maternal transfusion
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract Without Links:
NCC and AWHONN teaching materials describe that butorphanol, an opioid analgesic, characteristically produces a transient sinusoidal-like pattern or pseudo-sinusoidal pattern with moderate variability preserved.
This drug-related pattern has:
• smooth, regular oscillations
• maintained variability
• absence of true periodic decelerations
• resolution within 20–60 minutes
Simpson & Menihan describe butorphanol as producing a “saw-tooth, wavering pattern” often mistaken for dysrhythmia but actually benign.
True sinusoidal patterns (e.g., fetal-maternal hemorrhage) are fixed, smooth, non-variable patterns with absent variability, not matching the scenario.
Atrial flutter produces very rapid atrial contractions, which manifest as irregular baseline spikes—also not consistent.
Therefore, the described tracing aligns most closely with butorphanol effects.
(Full question statement)
The fetal heart rate tracing shown is obtained upon the woman's admission to labor and delivery. This tracing is most consistent with what maternal condition?
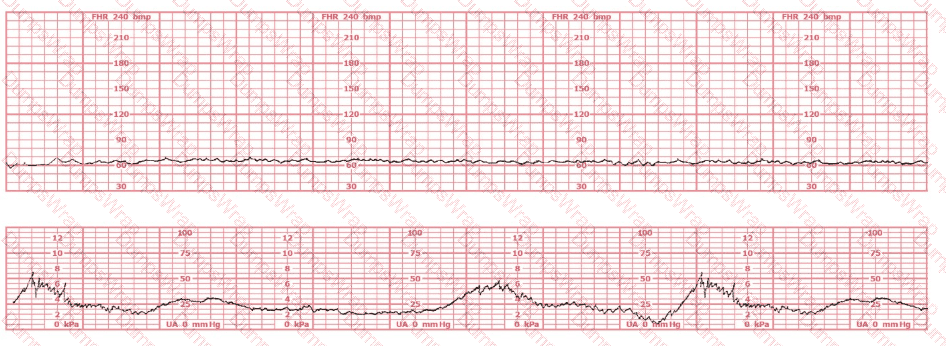
Options:
Eisenmenger's syndrome
Sickle cell anemia
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract (NCC C-EFM sources: AWHONN, Miller’s Pocket Guide, Menihan, Simpson, Creasy & Resnik, 2025 Candidate Guide)
The tracing displays baseline fetal bradycardia, with a rate near 100 bpm, minimal variability, and preserved periodic response. According to AWHONN’s Fetal Heart Monitoring Principles & Practices and Menihan’s Electronic Fetal Monitoring, maternal conditions that reduce oxygen-carrying capacity—including maternal anemia—can lead to lower fetal oxygen delivery, prompting a fetal compensatory bradycardic baseline.
Creasy & Resnik’s Maternal-Fetal Medicine notes that sickle cell anemia decreases maternal hemoglobin function even when maternal vital signs appear stable, reducing uteroplacental oxygen transport. Fetuses of mothers with sickling disorders may demonstrate lower resting fetal heart rates due to chronic mild hypoxemia.
Conversely, Eisenmenger’s syndrome is associated with severe maternal cyanosis and high fetal mortality, often producing late decelerations and growth restriction rather than mild bradycardia. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is commonly associated with heart block (especially with anti-Ro/SSA antibodies), which is not displayed here, as true heart block presents with a fixed atrial–ventricular dissociation and FHR < 60 bpm.
Thus, based on fetal physiology and maternal disease correlations taught in NCC-recommended sources, the tracing is most consistent with maternal sickle cell anemia.
Patient safety is enhanced when alarms:
Options:
Are determined by the unit leaders
Can be called by anyone
Occur infrequently
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
NCC and AWHONN emphasize unit-wide shared responsibility for:
Recognizing abnormal maternal or fetal findings
Calling for help
Triggering emergency responses (e.g., unit huddle, rapid response, safety pathways)
Safety culture requires:
Any staff member (RN, tech, provider) to initiate an alarm or escalate concern
No hierarchy delay
Rapid action when fetal compromise is suspected
Why the other answers are wrong:
A. Determined by unit leaders → incorrect; safety is team-wide, not hierarchical.
C. Occur infrequently → false; alarms must occur whenever needed, not limited.
Correct answer: B. Can be called by anyone.
A 45-year-old woman at 36-weeks gestation presents for a nonstress test. Vital signs are:
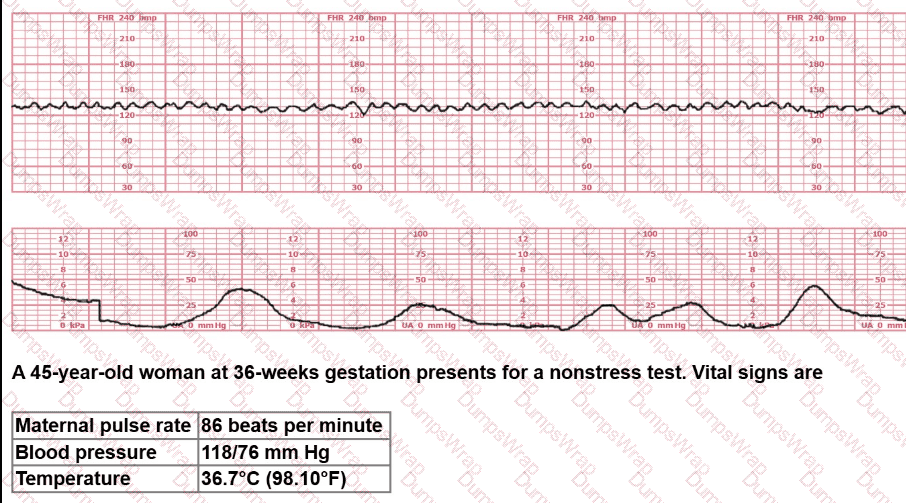
Maternal pulse rate: 86 beats per minute
Blood pressure: 118/76 mm Hg
Temperature: 36.7°C (98.1°F)
The next course of action would include:
Options:
Discharge home
Induce labor
Perform a Kleihauer-Betke test
Answer:
AExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
The NST strip shows:
Baseline FHR about 140 bpm
Moderate variability
Two or more accelerations meeting 15×15 criteria
No decelerations
Normal, infrequent contractions
Per NCC and AWHONN, a reactive NST is defined as:
≥2 accelerations of 15 bpm × 15 seconds in a 20-minute period
With baseline 110–160 and moderate variability
No recurrent decelerations
A reactive NST at 36 weeks in a hemodynamically stable mother with normal vitals is reassuring, and the appropriate disposition is routine follow-up and discharge.
Why the other options are incorrect:
B. Induce labor – Not indicated solely on maternal age or a reactive NST.
C. Kleihauer-Betke test – Used to quantify fetomaternal hemorrhage after trauma or sensitization risk; there is no such history here.
Therefore, the correct action is A. Discharge home.
During the second stage of labor, a period of bradycardia develops. The fetal heart rate baseline variability is moderate. The most likely cause of this bradycardia is:
Options:
Cord compression
Vagal stimulation
Vasospasm
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From NCC-Aligned Sources:
Second-stage bradycardia with moderate variability most commonly occurs from:
Vagal stimulation caused by head compression, particularly during descent and pushing.
Moderate variability indicates:
Neurologically intact fetus
Sufficient oxygen reserve
Temporary nature of bradycardia
This aligns with physiologic vagal slowing rather than hypoxic mechanisms.
Why the incorrect answers are wrong:
A. Cord compression → typically produces variable decelerations, not sustained bradycardia with preserved variability.
C. Vasospasm → associated with late decelerations and decreased variability (uteroplacental insufficiency).
Correct answer: B. Vagal stimulation
(Full question statement)
Interobserver reliability in interpretation of fetal heart rate tracings is greatest when the tracing is:
Options:
Abnormal
Indeterminate
Normal
Answer:
CExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract Without Links:
NCC examination standards and AWHONN clearly state that normal Category I patterns have the highest interobserver agreement because they contain objective, easily identifiable components:
• baseline 110–160 bpm
• moderate variability
• absence of late or variable decelerations
• presence or absence of accelerations
Simpson highlights that Category II tracings have poor reliability due to multiple combinations of variability and decelerations, while Category III patterns have higher agreement but occur far less frequently, limiting reliability measures.
Research cited within NCC-endorsed materials confirms that clinicians demonstrate the greatest agreement in identifying normal Category I patterns, making normal the correct answer.
====================================================
A woman at 36-weeks gestation comes in because of uterine contractions radiating to the back. She has no insurance. In accordance with the Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA), she is obligated to be:
Options:
Admitted without delay
Stabilized and receive a medical screening examination
Transferred to a safety-net hospital
Answer:
BExplanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract–Based NCC C-EFM References:
NCC’s Professional Issues domain includes EMTALA obligations for pregnant patients. EMTALA requires that ANY individual who presents to a hospital emergency department—regardless of insurance status—must receive:
A Medical Screening Examination (MSE)
Stabilization of any identified emergency medical condition (including labor)
No transfer unless the patient requests it or the hospital cannot provide necessary stabilizing care
This patient reports contractions at 36 weeks, which qualifies as a potential emergency medical condition until ruled out by the medical screening exam.
Correct obligations per EMTALA:
She must NOT be transferred solely due to lack of insurance (option C).
She does NOT need to be admitted unless labor is confirmed (option A).
She must receive a medical screening examination and stabilization (option B).
Thus, the correct answer is B. Stabilized and receive a medical screening examination.

