Palo Alto Networks SD-WAN Engineer Questions and Answers
When troubleshooting an issue at a site that is running on two cellular links from two carriers, the operations team shared some evidence shown in the graph below:
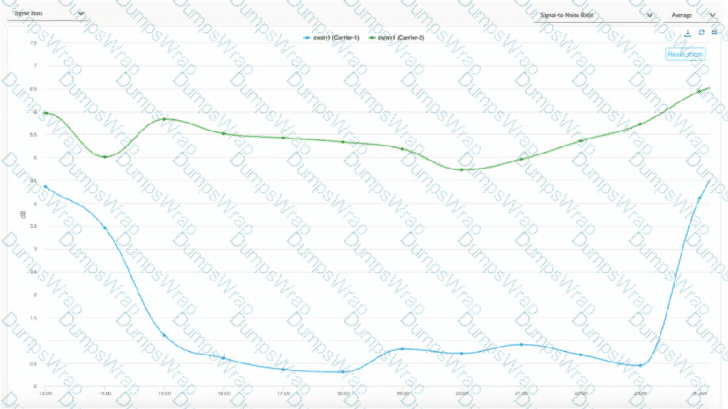
For the time duration shown in the graph, what are two inferences about the site’s traffic that can be made? (Choose two.)
In which modes can a Prisma SD-WAN branch be deployed?
A multinational company is deploying Prisma SD-WAN across North America, Europe, and Asia. The data centers in the North America region have served all regions, but regional policies are now being enforced that mandate each of the regions to build their own data centers and branch sites to only connect to their respective regional data centers.
How can this regionalization be achieved so that new or existing branch sites only build tunnels to the regional DC IONs?
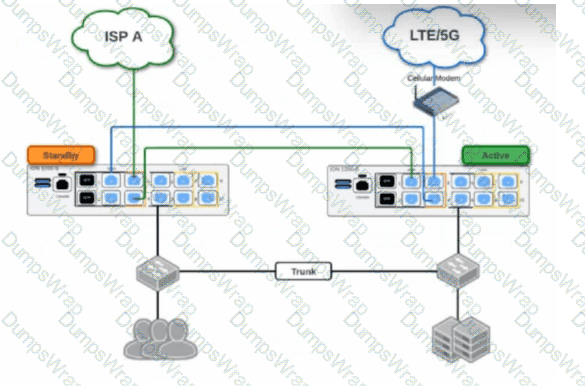
Based on the HA topology image below, which two statements describe the end-state when power is removed from the ION 1200-S labeled “Active”, assuming that the ION labeled “Standby” becomes the active ION? (Choose two.)
What is the default action for real-time media applications if link performance is poor?
What does Prisma SD-WAN use for monitoring and operations to deliver flow data and application visibility?
Which implementation allows Prisma SD-WAN to improve application performance for organizations facing inconsistent user experiences across branch locations, especially due to varying device types and network conditions, by using Layer 4 and Layer 7 optimization to boost throughput?
Which condition, when configured within a performance policy, is a trigger for generating an incident related to application performance or path degradation?
An administrator needs to generate a monthly report showing the "Top Applications" by bandwidth usage across all branch sites to justify a bandwidth upgrade.
Which specific component of the Prisma SD-WAN interface is designed to create, schedule, and email these PDF summaries?
For how many hours are Prisma SD-WAN VPN shared secrets valid?
Full discovery and classification of IoT devices by the IoT Security service is failing. Which Prisma SD-WAN ION device configuration will cause this behavior?
Return traffic for an application from the branch is being dropped on the branch ION. Application traffic arrives via SD-WAN internet overlay at the branch, and path policy for the application at the branch has the following settings:
Active = MPLS Overlay
Backup = Prisma Access on internet
Which branch configuration is the probable cause of this behavior?
A network engineer is troubleshooting an ION device that is showing as "Offline" in the Prisma SD-WAN portal, despite the site reporting that local internet access is working. The engineer has console access to the device.
Which CLI command should be used to specifically validate the device's ability to resolve the controller's hostname and establish a secure connection to it over a specific interface?
Which component of the Prisma SD-WAN solution is responsible for the deep application identification (App-ID) and the generation of flow metrics (Network Transfer Time, Server Response Time) at the branch?
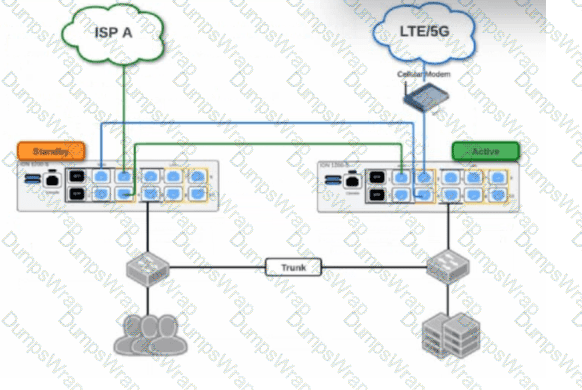
Based on the HA topology image below, which two statements describe the end-state when power is removed from the ION 1200-S labeled “Active”, assuming that the ION labeled “Standby” becomes the active ION? (Choose two.)
In the Prisma SD-WAN portal, an administrator is viewing the "Media" analytics for a branch site to troubleshoot complaints about poor voice quality.
When calculating the Mean Opinion Score (MOS) for voice traffic, which two metrics does the system prioritize active monitoring for, even when no user voice traffic is present on the link? (Choose two.)
A site has two internet circuits: Circuit A with 500 Mbps capacity and Circuit B with 100 Mbps capacity.
Which path policy configuration will ensure traffic is automatically shifted from a saturated circuit to the circuit with available bandwidth?
When planning a software upgrade for a large fleet of ION devices, what is the recommended best practice regarding the "Software Version" assigned in the Site Summary?
An organization has provided the following technical requirements and details:
High availability (HA) at all data center and branch locations
Two geographically separate main data center locations
One small data center location that contains local users and applications requiring policies
50 branch locations
ISP capacities for all branch locations but no accurate measurement of the actual bandwidth consumption
Based on Palo Alto Networks best practices and recommendations, which two licensing options will meet the customer objectives? (Choose two.)
In a Data Center deployment, what is the key functional difference between configuring a BGP neighbor as a "Core Peer" versus an "Edge Peer"?
A branch manager reports slow network performance, and the network administrator wants to use Prisma SD-WAN Copilot to quickly identify if a specific user, by source IP address, is consuming excessive bandwidth as well as which applications are contributing to this consumption. How can Copilot assist in this investigation?
Two branch sites, "Branch-A" and "Branch-B", are both behind active NAT devices (Source NAT) on their local internet circuits.
What requirement must be met for these two branches to successfully establish a direct Dynamic VPN (ION-to-ION) tunnel over the internet?
What are two requirements for implementing user/group-based path policies? (Choose two.)
An administrator wants to configure a Path Policy that routes all "Guest Wi-Fi" traffic directly to the internet using the local broadband interface, bypassing all VPN tunnels.
Which Service & DC Group setting should be selected in the policy rule to achieve this "Direct Internet Access" (DIA) behavior?
What is the primary function of the "CloudBlade" platform in a Prisma SD-WAN deployment when integrating with third-party services or Prisma Access?

